Programming Fundamentals
Learn programming fundamentals understand computer programs, types of programming languages, and C++ basics for beginners.
What Is a Computer Program?
A computer program is a set of instructions written in a programming language that tells a computer what to do. Since computers can’t think or make decisions, they rely entirely on the instructions we give them.
A programmer writes these instructions using programming languages like C++, Python, or Java. In simple words:
Programming = Communicating with a computer in a language it understands.

Advantages of Computer Programs
- Solve complex problems through logical instructions.
- Perform repetitive tasks quickly and efficiently.
- Handle large amounts of data with ease.
- Display results in various styles or formats.
- Improve productivity by automating workflows.
From hospitals to finance, computer programs are everywhere simplifying lives and accelerating progress.

For more: Introduction to Problem Solving Programming Fundamentals
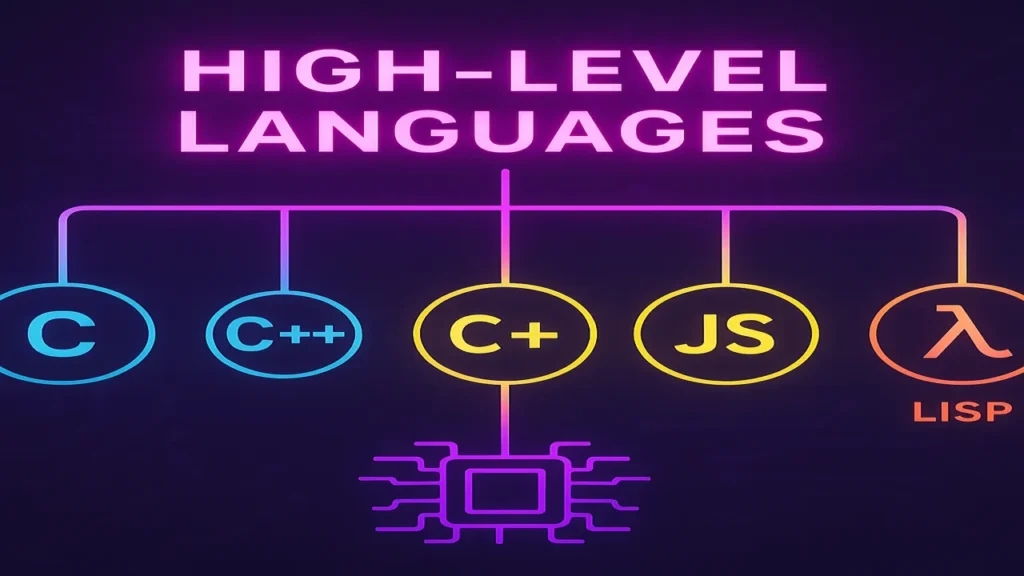
What Are Programming Languages?
A programming language is a medium for humans to communicate with computers. It defines rules, syntax, and commands that let programmers write code the machine can understand.
Computers natively understand only machine language (0s and 1s), so higher-level languages were developed to make coding easier. These human-readable instructions are later converted into machine code using compilers or interpreters.
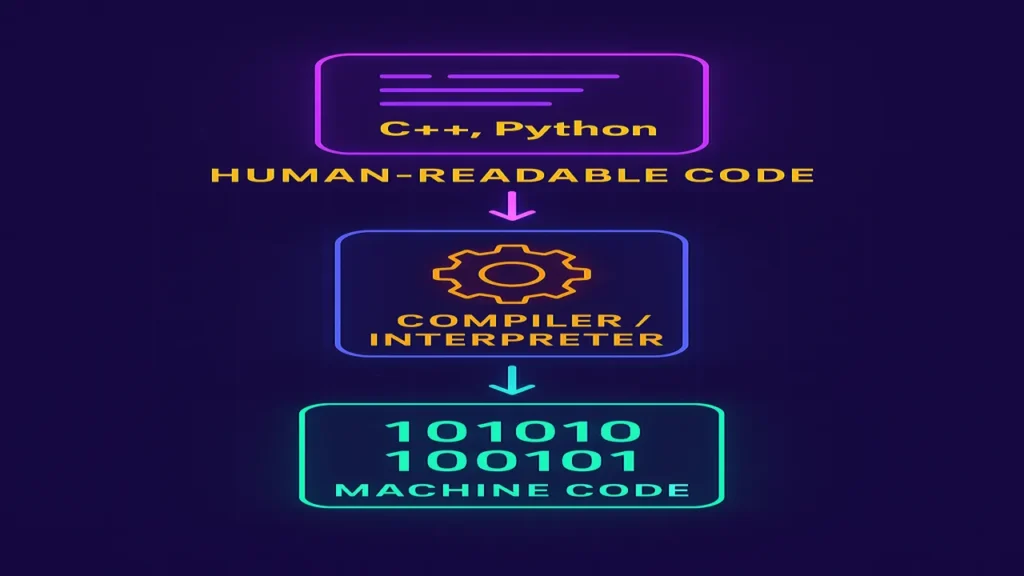
Types of Programming Languages
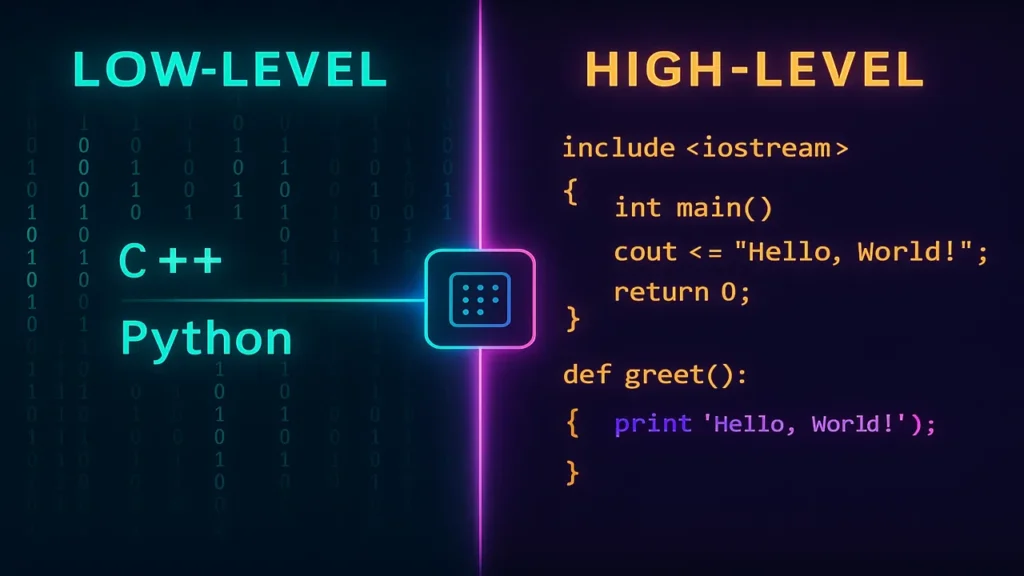
1. Low-Level Language
- Works close to the hardware.
- Uses binary or symbolic instructions.
- Fast and memory-efficient but difficult to write.
Examples: Machine Language, Assembly Language
2. High-Level Language
- Closer to human language and easier to use.
- Uses English-like syntax.
- Requires compiler or interpreter.
Examples: C, C++, Python, Java
For More: Introduction to Data Structures 2025
Understanding Low- and High-Level Languages (Real-Life Analogy)
- Low-Level: Like a mechanic controlling every car component manually the engine, gears, wiring.
- High-Level: Like a driver using steering and pedals the system handles the rest.

Types of Low-Level Languages
1. Machine Language
- Written in 0s and 1s (binary).
- Directly executed by the computer.
- Fast but extremely hard for humans to write.
2. Assembly Language
- Uses mnemonics like
MOV,ADD,SUB. - Requires an assembler to translate code.
- Easier than binary but still close to hardware.

Types of High-Level Languages
1. Procedural Language
- Step-by-step instructions.
- Uses loops, conditionals, and functions.
Example: C, Fortran, Pascal
2. Object-Oriented Language
- Organizes data into classes and objects.
- Promotes reusability through inheritance and encapsulation.
Example: C++, Java, Python
3. Scripting Language
- Interpreted line by line, ideal for automation.
Example: JavaScript, PHP, Python
4. Functional Language
- Based on mathematical functions and pure logic.
Example: Lisp, Haskell
What Is C++?
C++ is a powerful, high-level programming language created at Bell Labs in 1980. It combines the efficiency of C with the flexibility of object-oriented programming.
Key Features
- OOP (Classes, Inheritance, Polymorphism)
- Procedural Support (functions and structures)
- Standard Template Library (STL)
- High Performance — close to hardware
- Portability — runs on multiple platforms
C++ is widely used in game development, operating systems, and high-performance applications.
What Is Code?
Code is the set of instructions that computers execute to perform specific tasks. Each line in a program represents a command.
There are two types of code:
1. Source Code
- Human-readable text written in programming languages.
- Example:
cout << "Hello, World!";
2. Object Code
- Machine-readable version of compiled source code.
- Example: Compiled file like
program.obj.
Analogy:
Writing source code is like writing a recipe; compiling it produces the finished dish.

Basic Programming Structure in C++
Every program is built from constructs and building blocks the core ingredients of logic and structure.
1. Constructs
Keywords and syntax that define how code operates.
Examples: if, for, while, class, function
2. Building Blocks
Elements that make up the program: variables, constants, functions, arrays, and objects.
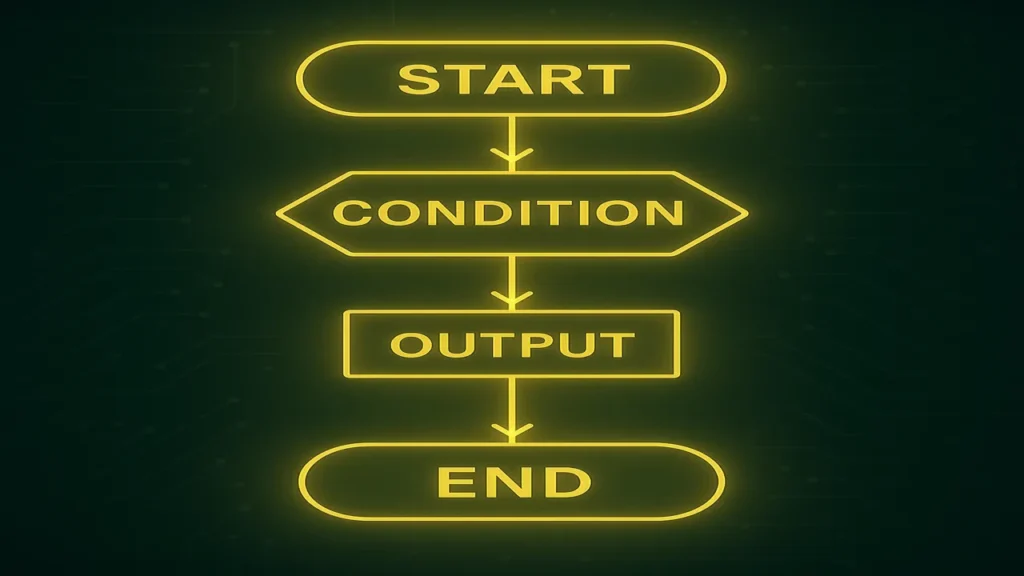
Logic, Control Flow, and Structure
- Logic: Step-by-step reasoning that drives a program’s decisions.
- Control Flow: The sequence in which statements execute (
if,else,for,while). - Structure: Organizing code into readable, modular parts (functions, classes).
Common Constructs in C++
| Construct | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Variables & Constants | Store data |
| Data Types | Define the kind of data |
| Operators | Perform actions on data |
| Control Structures | Manage execution flow |
| Functions | Reusable modular code |
| Arrays & Strings | Store multiple values |
| Pointers & References | Manage memory |
| Classes & Objects | Encapsulate data and behavior |

Conclusion
Programming is not just about writing code it’s about teaching computers to think logically and perform actions efficiently. By understanding the fundamentals from languages to structures you build the foundation for mastering advanced topics like AI, data science, and software engineering.
🌟 Remember: Every great programmer once started with “Hello, World.”




Conditional Statements, Comments and Syntax in C++