Basics of C++ Programming
Master the basics of C++ programming with this beginner-friendly guide from ElecturesAI. Learn how C++ programs are structured, understand the role of header files, variables, constants, data types, operators, and control structures.
Anatomy of a Simple C++ Program
Every C++ program begins with certain foundational components:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, World!";
return 0;
}Each line here serves a purpose:
#include <iostream>→ imports tools for input/output.using namespace std;→ lets us usecoutandcinwithout prefixes.int main()→ is the entry point of the program.cout <<→ displays output on screen.return 0;→ signals successful completion.

For More Programming Fundamentals: Understanding Computer Programs, Languages, and C++ Basics
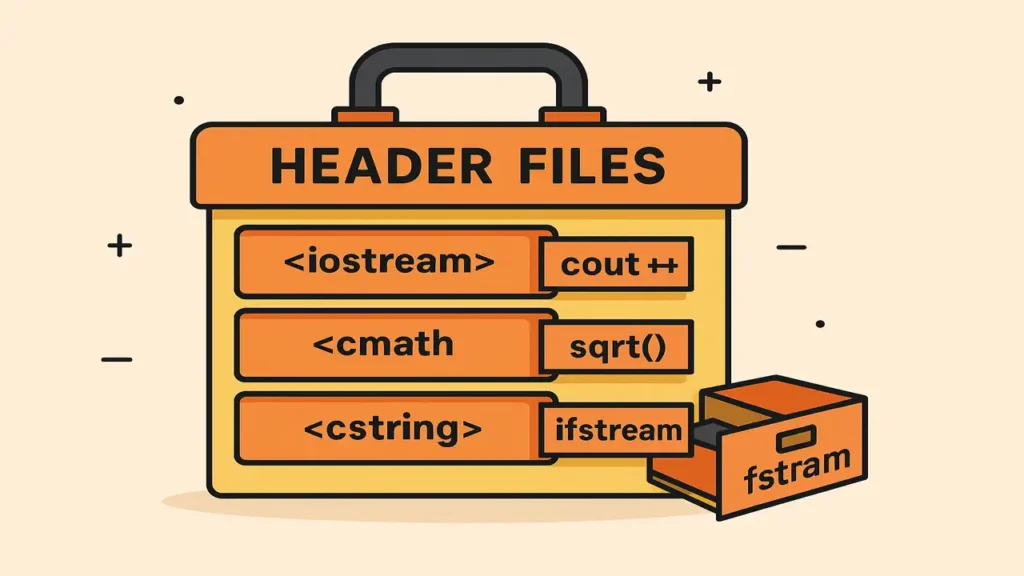
Header Files Your Code Toolbox
A header file is like a library shelf filled with ready-made functions, constants, and classes you can use in your own code.
For example:
<iostream>handles input/output<cmath>provides math functions likesqrt()<cstring>works with strings<fstream>handles file operations
Why use header files?
- Reuse pre-written code
- Keep your program organized
- Make maintenance easier
Preprocessor Directives The Setup Phase
Before your code even compiles, the preprocessor runs. Think of it as the preparation step before cooking gathering all the necessary ingredients.
Commands like #include or #define instruct the compiler to include external resources or define constants before compilation.

For More. Introduction to Problem Solving Programming Fundamentals
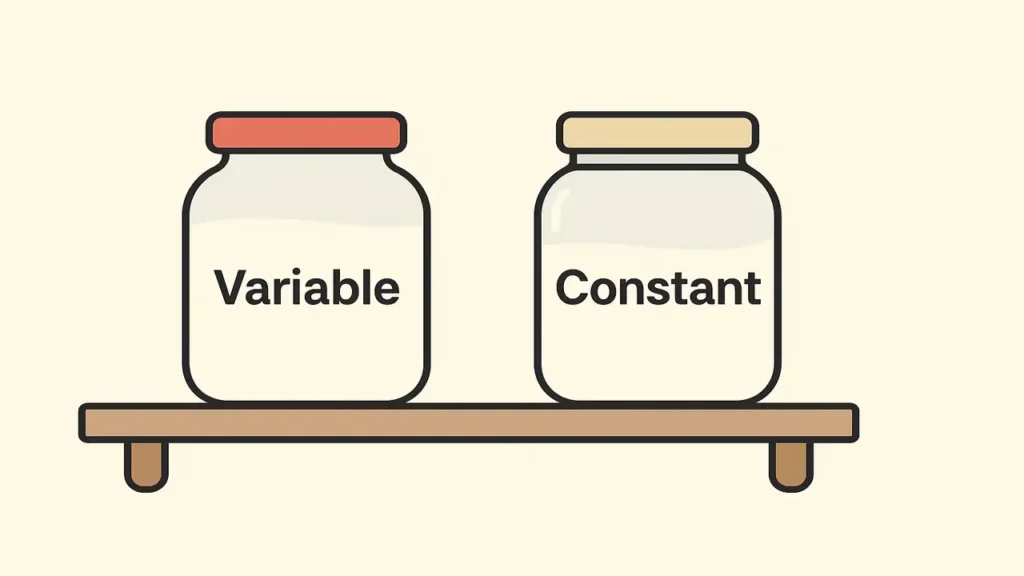
Variables and Constants Data Containers
Variables act as containers that store changing data; constants store fixed data.
Example:
int age = 25;
const double PI = 3.14159;- Variables can change values during execution.
- Constants remain fixed.
Naming Rules:
- Must begin with a letter or underscore.
- Case-sensitive (
Age≠age). - Should describe purpose clearly.
Data Types Defining What You Store
Data types tell the compiler what kind of data a variable holds.
They define memory size, value range, and valid operations.
Categories:
- Built-in:
int,float,double,char,bool,void - Derived: arrays, pointers, functions
- User-defined:
struct,class,enum
Real-Life Analogy:
Making tea uses multiple data types:
int cups = 2;float sugarQty = 1.5;char milkType = 'C';bool teaReady = true;string teaName = "Kashmiri Tea";

Operators Performing Actions
Operators are the symbols that perform calculations or comparisons.
Arithmetic: + - * / %
Relational: == != > < >= <=
Logical: && || !
Assignment: = += -= *= /=
Example:
int a = 10, b = 5;
int sum = a + b;
bool check = (a > b);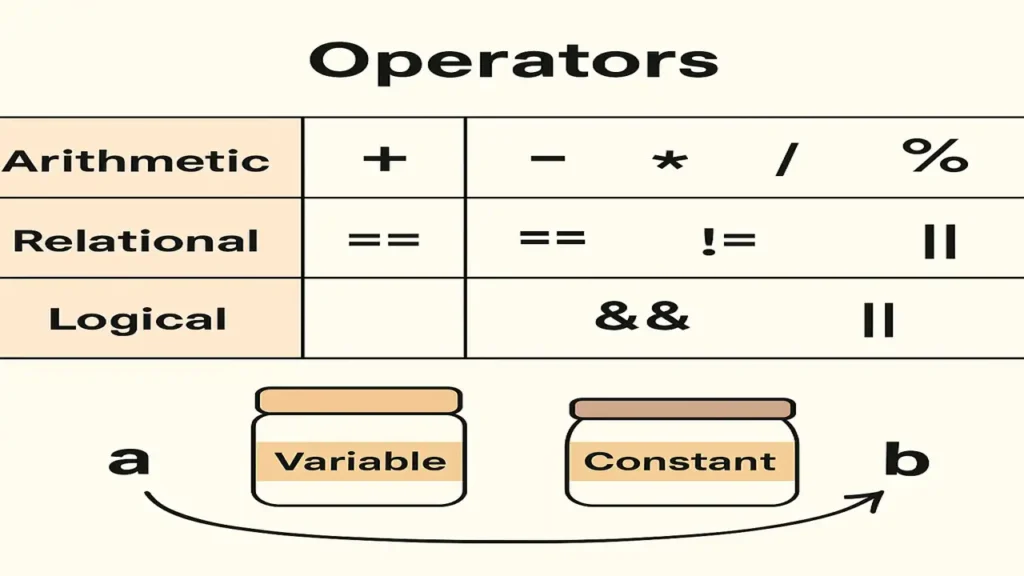
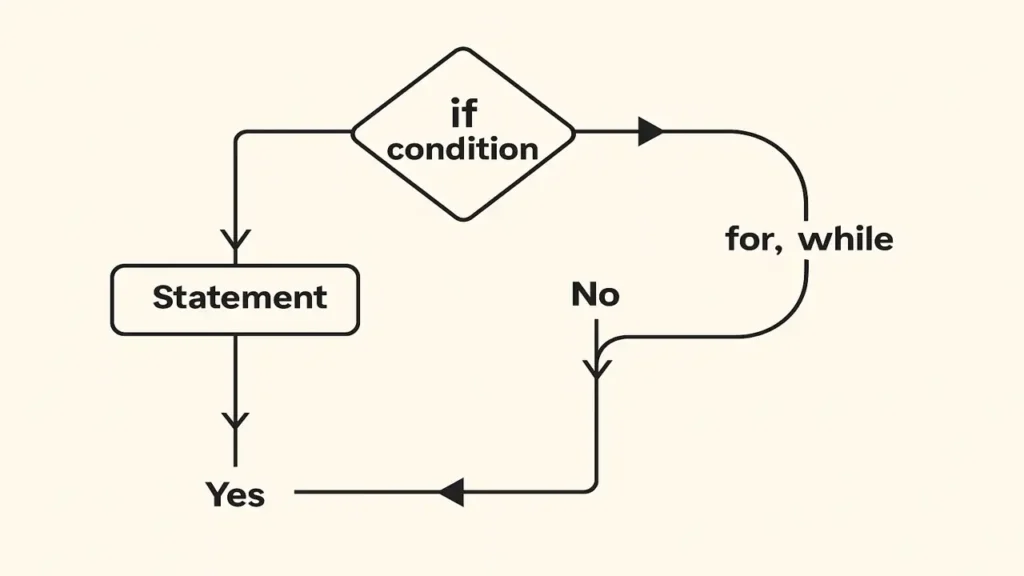
Control Structures Directing the Program Flow
Programs make decisions and repeat actions using control structures:
Decision Making:
if (age >= 18)
cout << "Adult";
else
cout << "Minor";Loops:
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
cout << i;Jump Statements:break, continue, return
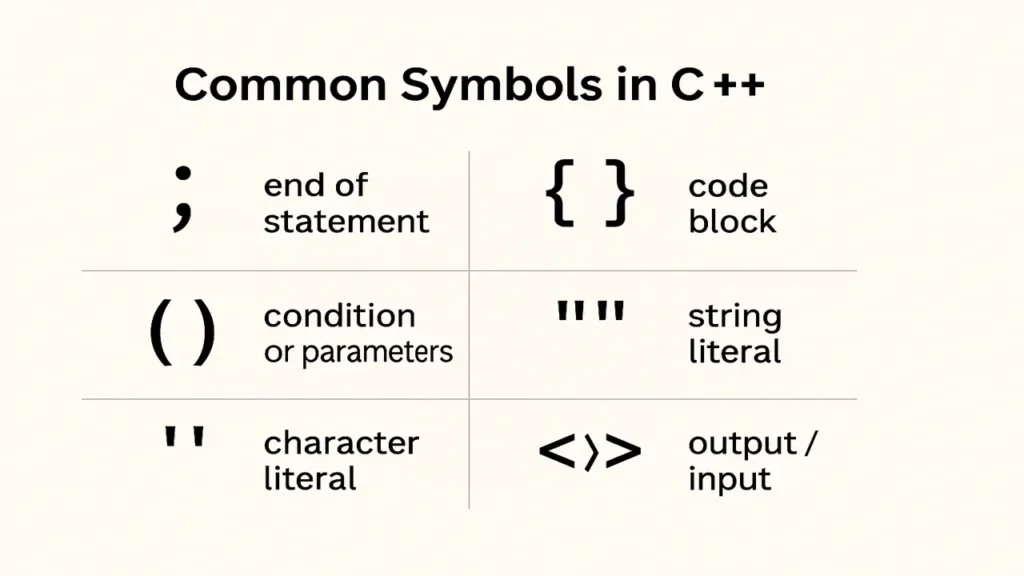
Common Symbols in C++
Every punctuation mark in C++ has a purpose:
;ends a statement{}define blocks()wrap conditions or parameters""and''hold strings or characters<<and>>handle output/input
Conclusion
Learning C++ begins with understanding these fundamental blocks: header files, variables, data types, operators, and control structures. Once you master these, you can build logical, efficient programs from simple calculators to complex systems.



Conditional Statements, Comments and Syntax in C++