Intelligent Software Engineering
Discover how Intelligent Software Engineering merges AI and software development to build smarter, adaptive systems that learn, reason, and evolve efficiently.
ISE is shaping the next generation of smart, autonomous software systems that not only serve users but think with them.
What Is Intelligent Software Engineering?
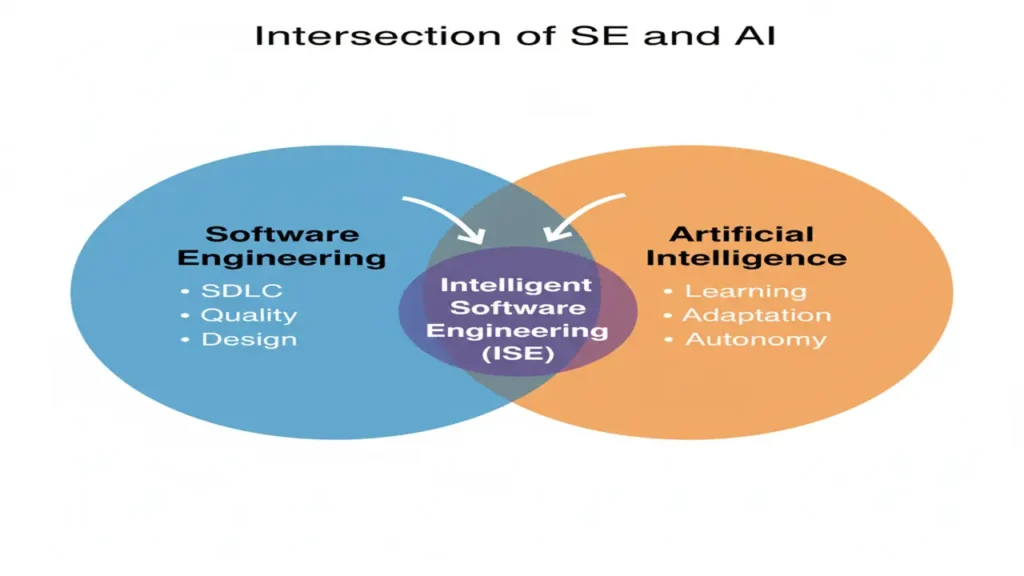
Intelligent Software Engineering (ISE) integrates AI and ML techniques across the entire Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) to enhance automation, reasoning, and adaptability.
It bridges two domains:
| Discipline | Core Focus |
|---|---|
| Software Engineering (SE) | Structured processes, design principles, and quality assurance. |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Learning, adaptation, and decision-making capabilities. |
ISE serves a dual purpose:
- Engineering with Intelligence Using AI tools to support developers (e.g., GitHub Copilot).
- Engineering of Intelligent Systems Building AI-centric products like chatbots or recommendation engines.
Lecture 1 – Introduction to Programming Paradigms
Why Intelligent Software Engineering Matters
Traditional software engineering faces recurring challenges from managing complexity to ensuring adaptability. ISE addresses these pain points using intelligent automation.
| Challenge | Traditional SE Approach | ISE Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Manual documentation and adherence | NLP-based requirement analysis |
| Productivity | Adding more developers | AI-assisted code generation |
| Quality & Bugs | Manual code reviews and testing | Predictive debugging with ML models |
| Adaptability | Manual redeployment | Self-healing and autonomous systems |
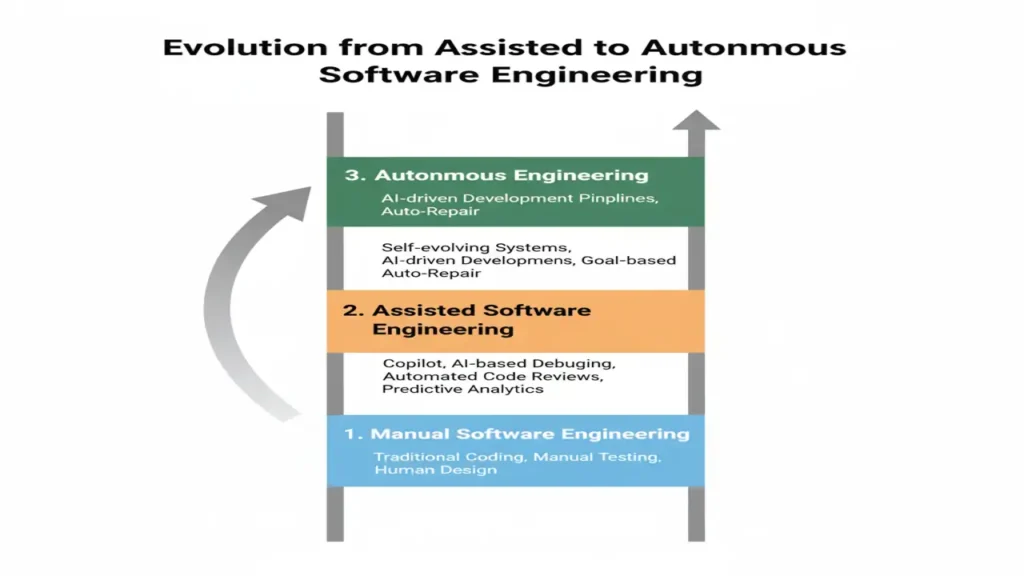
ISE’s ultimate goal is to transition from assisted engineering (AI as a helper) to autonomous engineering (AI as an active participant).
Core Concepts in Intelligent Systems
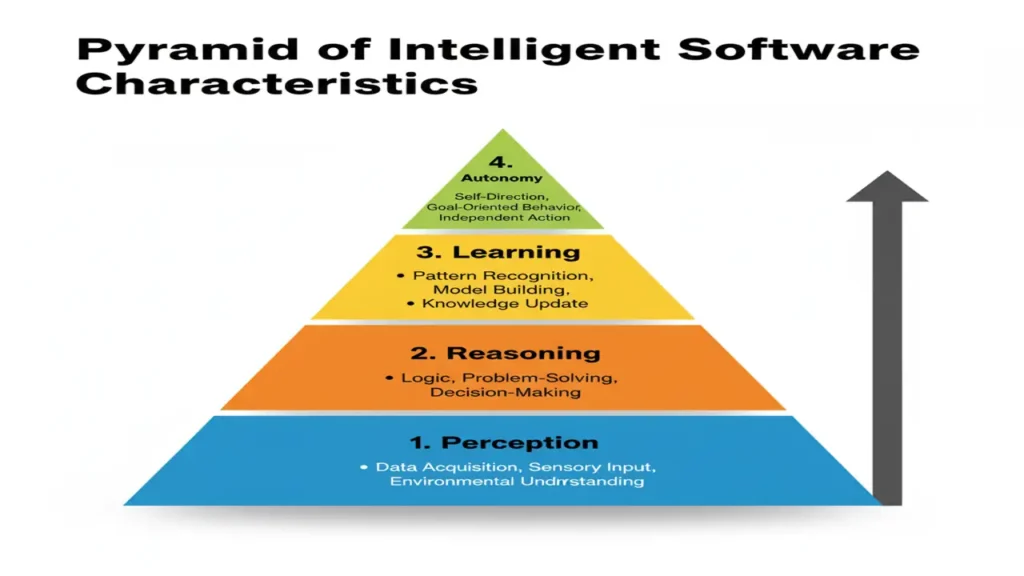
To understand ISE, we must understand what makes software intelligent. These systems rely on core AI principles:
1. Intelligent Agents
Software entities that perceive their environment and act to achieve specific goals.
Example: An AI bug-fixing bot analyzing code commits and proposing corrections.
2. Autonomy
The ability to operate without human intervention.
Example: A fraud detection system that can automatically block suspicious transactions.
3. Adaptability (Learning)
Systems that learn from experience and improve performance using ML algorithms.
Example: A recommendation system refining suggestions from user behavior.
4. Reasoning
Drawing logical conclusions from available data.
Example: A design assistant reasoning about component compatibility in complex architectures.
Historical Evolution and Modern Trends
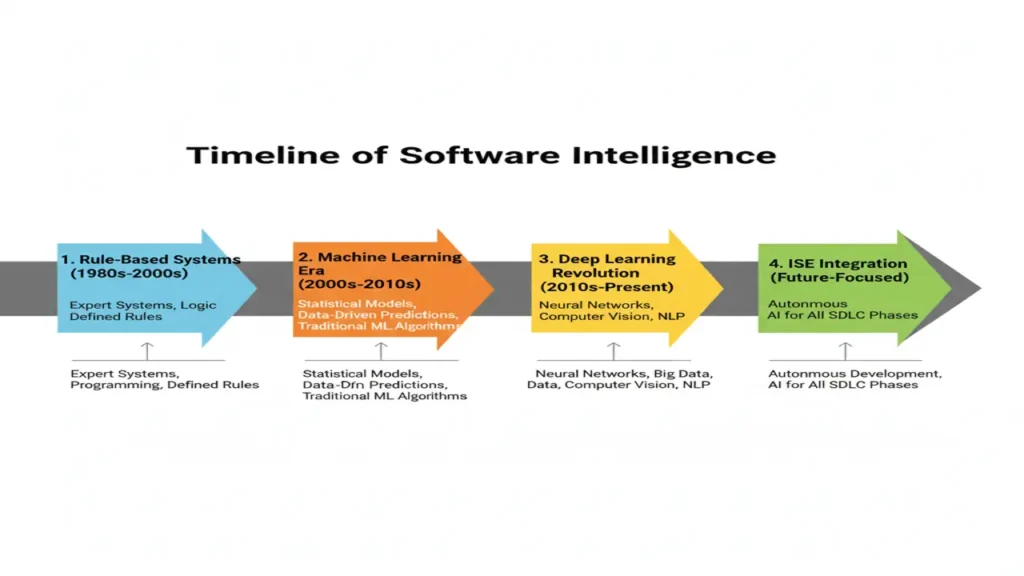
Early Days (1970s–1990s)
Software engineering relied heavily on rule-based expert systems, but these were rigid and couldn’t handle complex, dynamic scenarios.
The Modern Era (2010s–Now)
Advancements in machine learning, big data, and GPUs enabled scalable, data-driven intelligence. This evolution birthed today’s Intelligent Software Engineering.
Current Trends Shaping ISE
- MLOps: Streamlining ML deployment and monitoring in production.
- AI-Powered Tools: From GitHub Copilot to ChatGPT boosting developer productivity.
- Search-Based Software Engineering (SBSE): Using evolutionary algorithms for optimization problems like test case generation.
Conclusion
Intelligent Software Engineering isn’t a futuristic concept it’s the present transformation of how we design, build, and maintain systems.
By merging human creativity with AI intelligence, ISE marks the shift from code written by humans for machines to systems that learn, reason, and evolve with humans.
“Intelligent Software Engineering isn’t just about teaching machines to think it’s about training our minds to build systems that learn, adapt, and grow with us.
Every line of intelligent code you write is a reflection of your own intelligence evolving.”




