Core AI/ML Concepts
Understand the core AI/ML concepts every software engineer should know from supervised learning to data preprocessing and key algorithms like regression and classification.
In this lecture, we dive into the fundamental building blocks of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) the driving forces behind Intelligent Software Engineering (ISE).
Understanding these concepts helps engineers build software that learns, adapts, and improves over time.
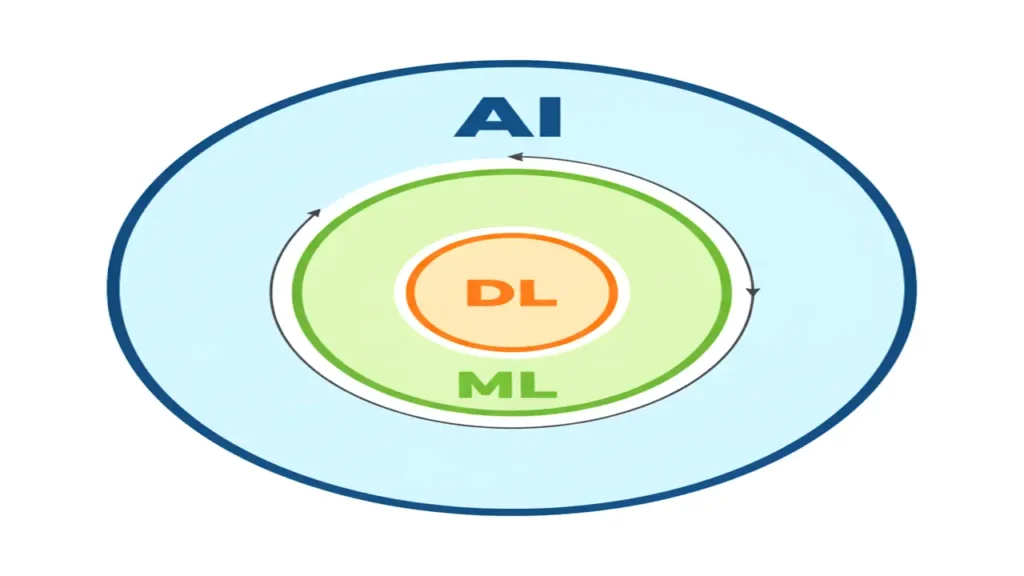
Overview of AI, ML, and Deep Learning (DL)
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is the broader concept of creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence such as reasoning, learning, or decision-making.
Machine Learning (ML)
ML is a subset of AI focused on enabling machines to learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed. The key idea: “learn from experience.”
Deep Learning (DL)
DL is a further specialization of ML that uses artificial neural networks to process large-scale, complex data (like images, speech, and text).
Deep Learning powers today’s vision models, chatbots, and recommendation systems.
Review of Software Engineering Principles
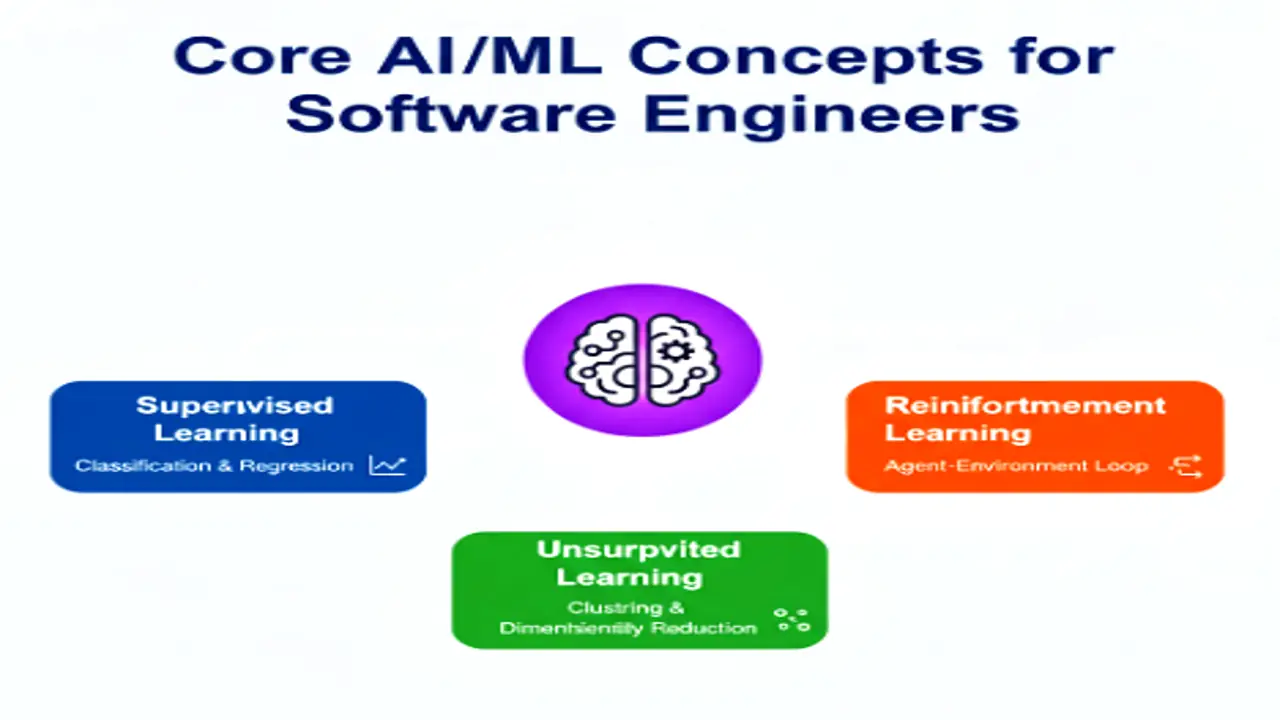
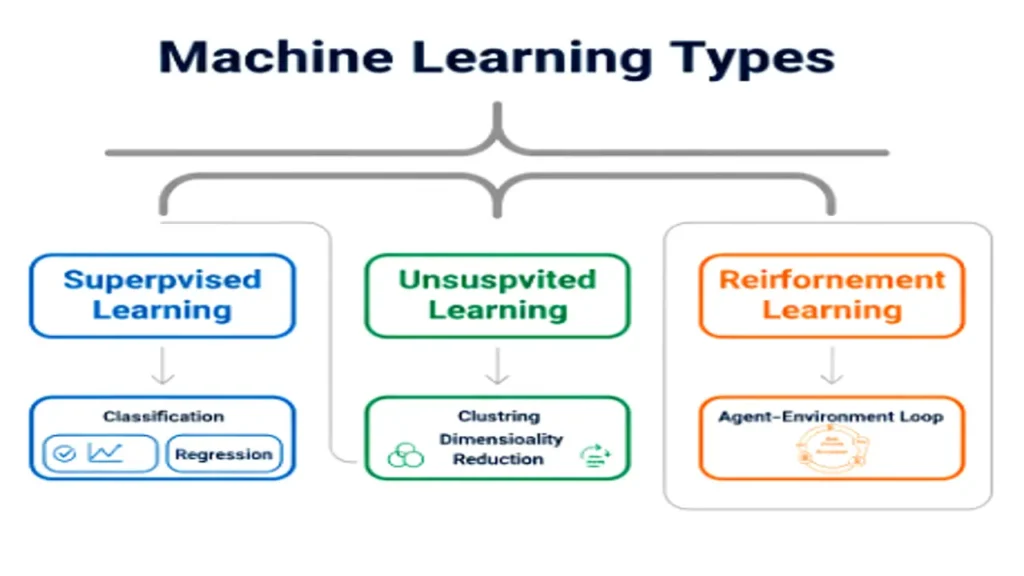
Types of Machine Learning
Machine Learning techniques can be grouped into three main types each serving a different purpose.
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Model learns from labeled data (input-output pairs). | Email spam detection, credit risk analysis. |
| Unsupervised Learning | Model finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data. | Customer segmentation, anomaly detection. |
| Reinforcement Learning (RL) | Model learns through reward-based feedback from its environment. | Game-playing AI, robotic control, self-driving cars. |
Data Essentials in Machine Learning
Data is the fuel of any intelligent system. Poor data quality can limit even the most advanced model.
Feature Engineering
The process of selecting and transforming input variables (features) to help models learn better.
Example: Extracting “average session time” from raw app logs for a churn prediction model.
Data Preprocessing
Includes cleaning, normalization, handling missing values, and encoding categorical data ensuring consistent, usable input.
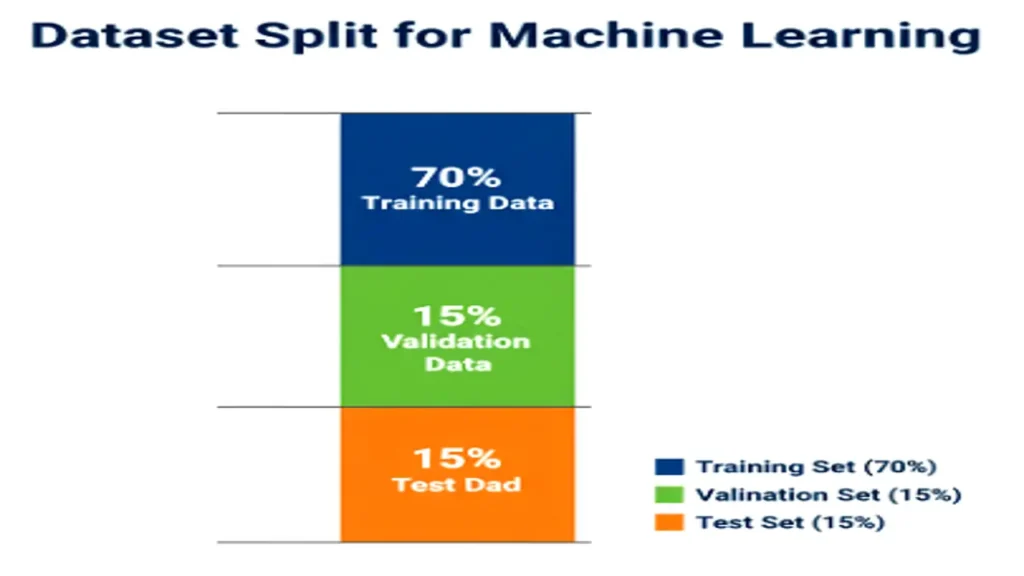
Training, Validation, and Test Sets
- Training Set: Used to train the model.
- Validation Set: Helps tune hyperparameters and avoid overfitting.
- Test Set: Evaluates final model performance on unseen data.
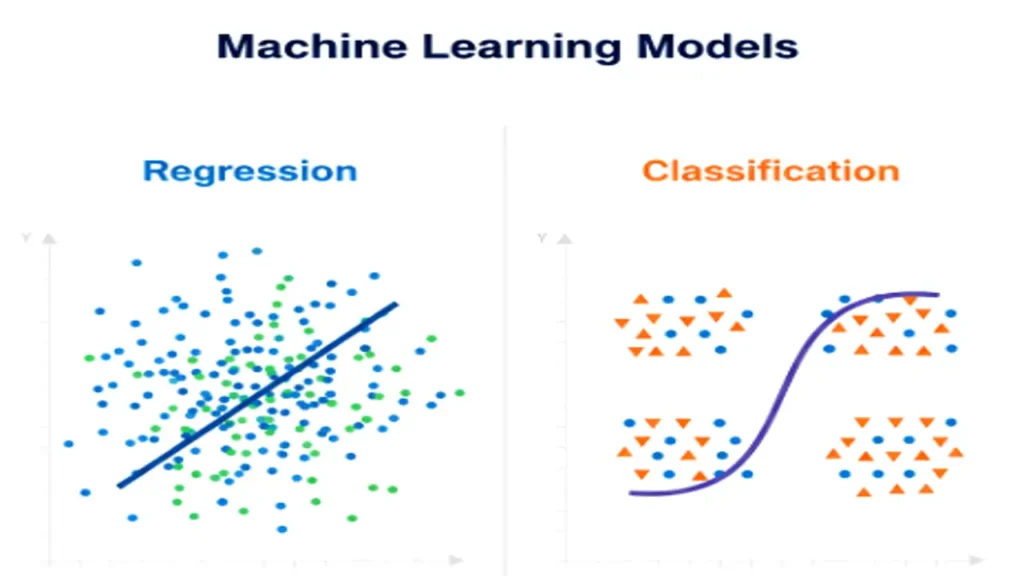
Key ML Algorithms: Regression & Classification
Machine Learning starts with understanding two foundational problem types:
Regression
Used when predicting continuous values.
Example: Forecasting temperature, sales, or housing prices.
Popular Algorithms: Linear Regression, Ridge Regression, Decision Trees.
Classification
Used when predicting discrete categories.
Example: Predicting whether an email is spam or not spam.
Popular Algorithms: Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Support Vector Machines (SVM).
Why These Concepts Matter for Software Engineers
Understanding these fundamentals empowers engineers to:
- Build data-driven applications that improve automatically.
- Integrate predictive analytics into existing systems.
- Collaborate effectively with data scientists and ML engineers.
- Prepare for advanced ISE topics like AI-assisted coding, MLOps, and self-healing systems.
Summary
- AI enables reasoning and problem-solving.
- ML empowers software to learn from data.
- DL scales this learning through neural networks.
- Understanding data processing, model training, and algorithm basics forms the foundation of Intelligent Software Engineering.
“Data teaches us what the world looks like intelligence teaches us what it could become.”