Network Sniffing and Hijacking
Learn about Network Sniffing and Hijacking techniques, including ARP spoofing, session hijacking, and defenses to protect against these attacks. Understand how these methods work and the best practices for safeguarding your network security.
Introduction: Mastering Network Sniffing and Hijacking
Network sniffing and hijacking are powerful techniques used in penetration testing and cyberattacks. These attacks allow attackers to intercept and manipulate network traffic, creating significant security risks. In this blog, we’ll delve into the mechanics of network sniffing, ARP spoofing, session hijacking, and defenses against them.

What is Network Sniffing?
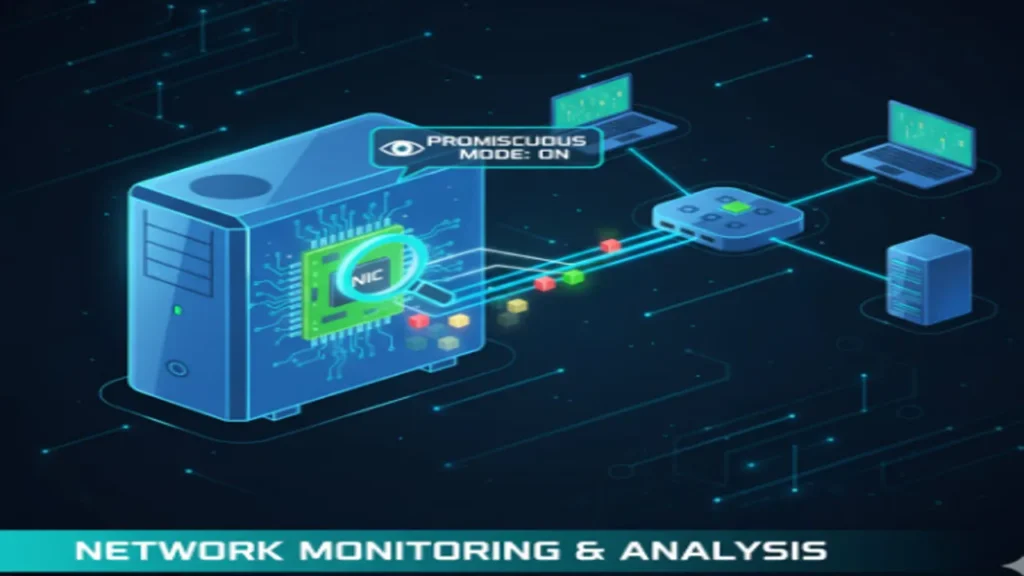
Network sniffing, also known as packet analysis, involves capturing and inspecting data as it travels over a network. It allows attackers to gather sensitive information like passwords, emails, and browsing history. Understanding sniffing techniques is essential for both attackers and defenders.
Key Concepts:
- Promiscuous Mode: Essential for sniffing tools, enabling the NIC to capture all traffic.
- The Problem of the Switch: Traditional sniffing methods fail on switched networks, requiring active sniffing techniques.
How Hackers Break In and Stay Hidden: Inside Advanced Cyber Attack Vectors
Sniffing Tools You Need to Know
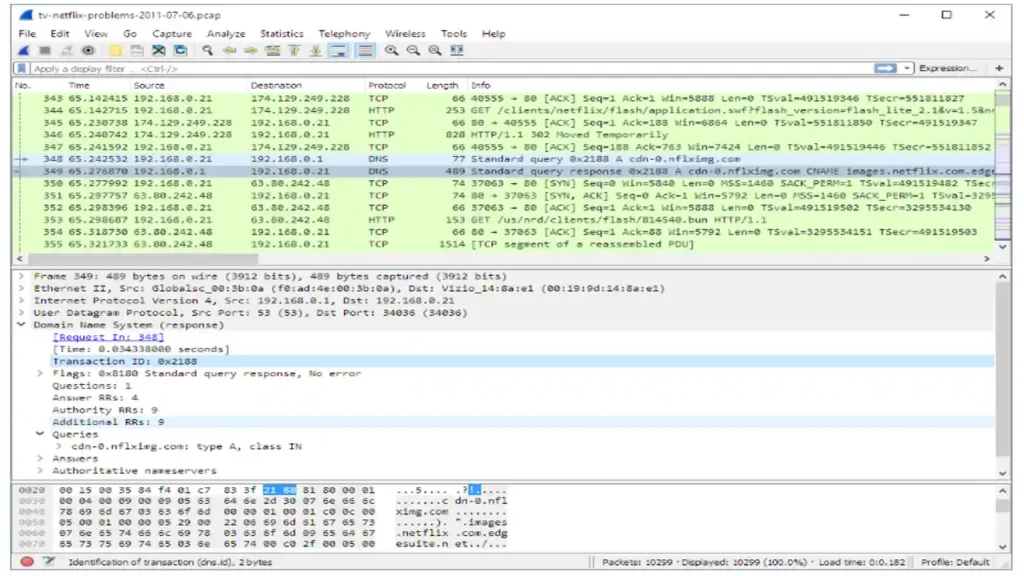
Several tools allow attackers and defenders to analyze network traffic, such as Wireshark and tcpdump.
- Wireshark: A graphical tool for deep packet inspection.
- tcpdump: A command-line utility for network packet capture.
- tshark: A command-line version of Wireshark for advanced packet filtering.
Passive vs. Active Sniffing
- Passive Sniffing: Ideal for hub-based or Wi-Fi networks, where the attacker simply listens for broadcasted traffic.
- Active Sniffing: Used on switched networks, where attackers inject malicious packets to redirect traffic to their device.
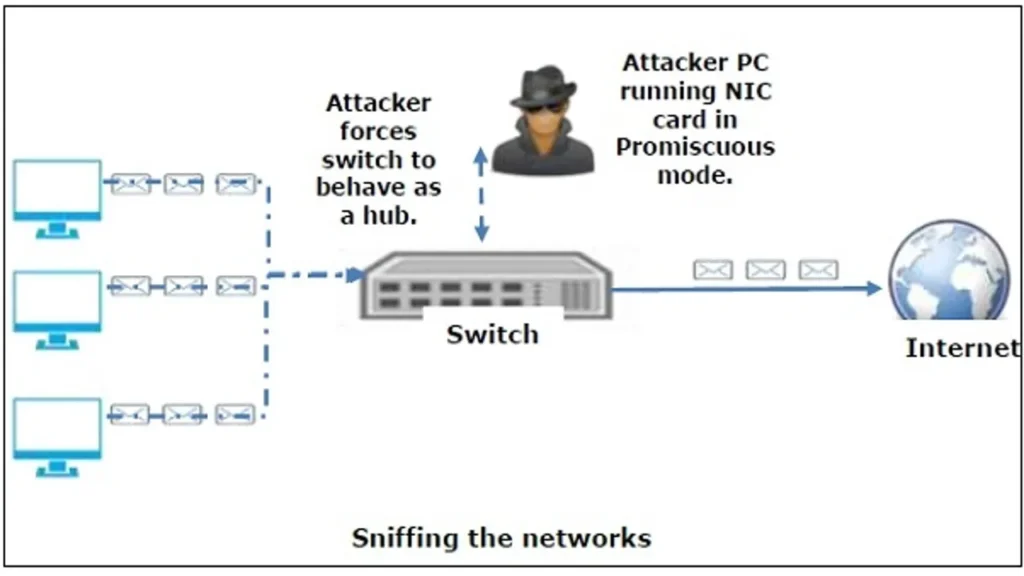
The Power of Spoofing: ARP, MAC, and DNS Attacks
Network sniffing can escalate to hijacking with attacks like ARP spoofing, MAC flooding, and DNS spoofing. These attacks manipulate traffic and can steal data or redirect it to malicious servers.
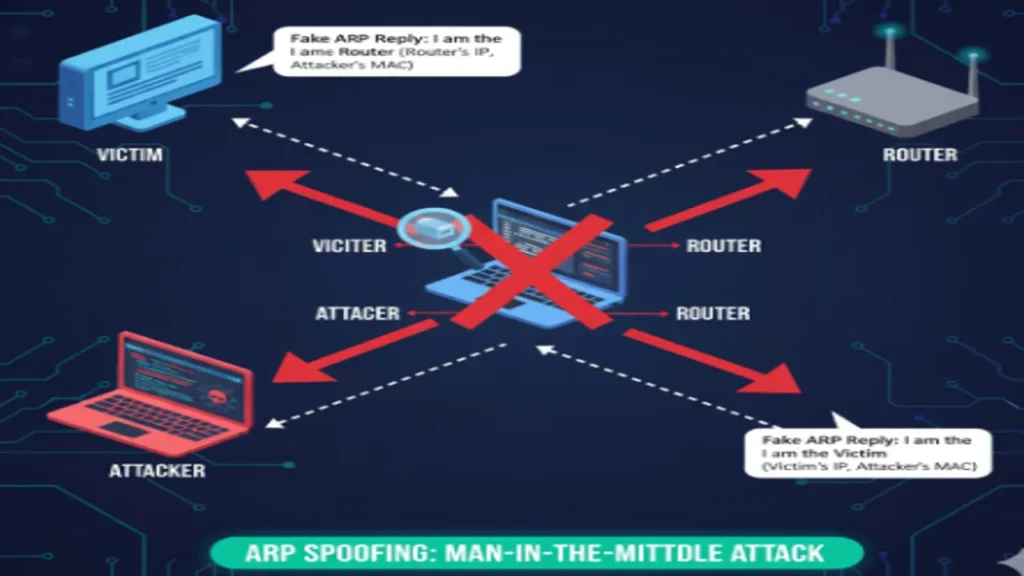
ARP Spoofing
ARP Spoofing allows attackers to intercept traffic between the victim and router by sending fraudulent ARP messages.
Defense: Implement Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) on switches to verify ARP replies.
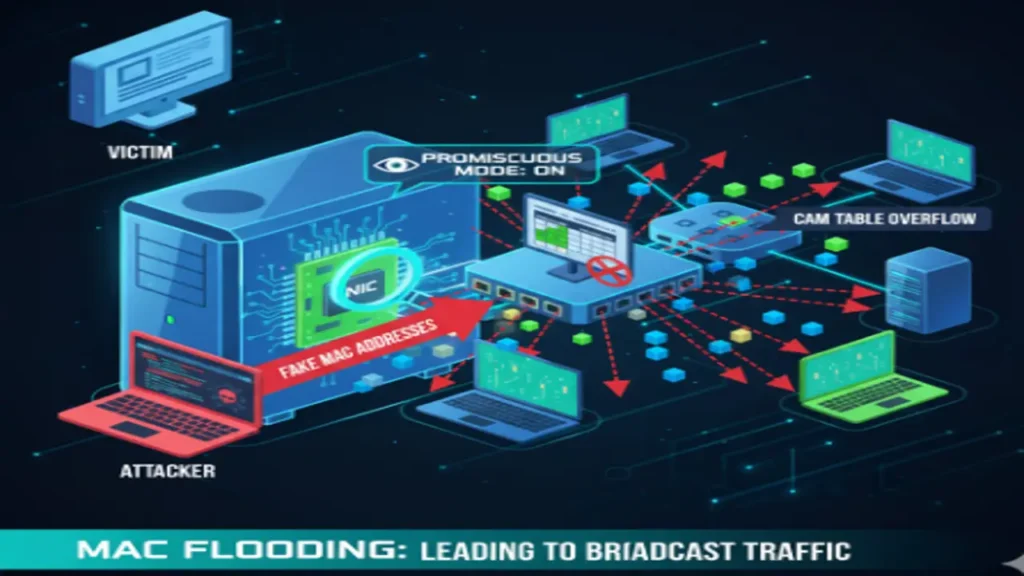
MAC Flooding and Spoofing
- MAC Flooding: Fills a switch’s CAM table with fake MAC addresses, causing the switch to broadcast all traffic.
- MAC Spoofing: Changing the MAC address to bypass network security.
Defense: Implement port security on switches.
DNS Spoofing
This attack poisons the DNS cache, redirecting victims to malicious websites.
Defense: Use DNSSEC for cryptographic DNS lookup validation.

Session Hijacking: Taking Control of Active Sessions
Session hijacking occurs when attackers steal a session token, allowing them to impersonate the legitimate user.
Methods of Hijacking
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Stealing session cookies from a victim’s browser.
- Session Sidejacking: Using sniffing tools to capture session cookies from unencrypted traffic.
- Session Fixation: Attacker pre-assigns a session ID, tricking the victim into logging in with it.
Defense: Enforce HTTPS, use HttpOnly cookies, and implement session timeouts.
Protecting Against Sniffing and Hijacking Attacks
While network sniffing and hijacking are potent threats, there are key defenses to safeguard against them.
Defensive Strategies:
- Enforce HTTPS: Encrypt all traffic to prevent session sidejacking.
- HttpOnly Cookies: Protect session cookies from being accessed by malicious scripts.
- Session Timeout: Automatically expire sessions after inactivity.
- IP/User-Agent Correlation: Match session tokens with their originating IP and browser to detect hijacking.
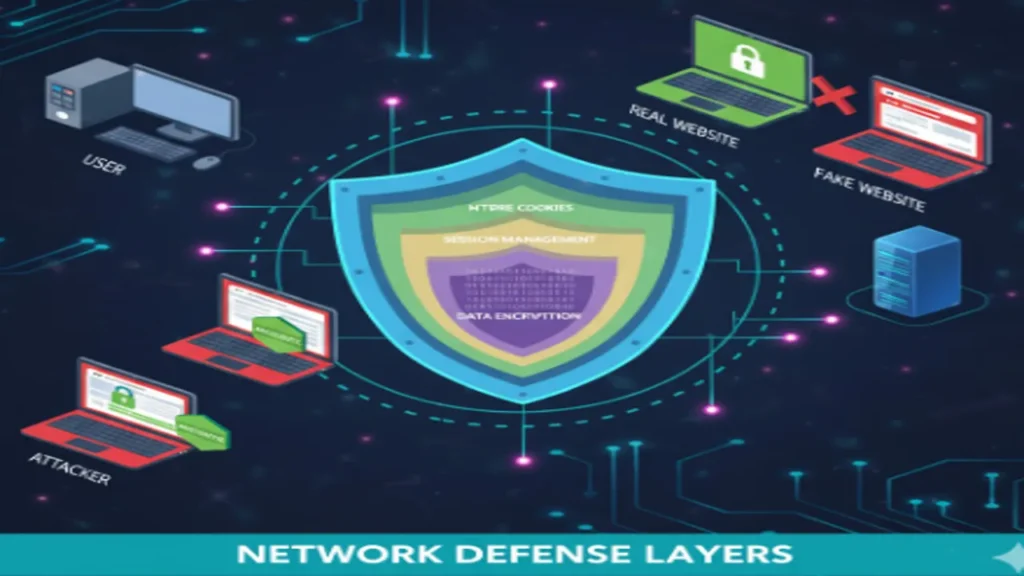
Conclusion: Strengthen Your Network Defenses
To protect against sniffing and hijacking attacks, network security practitioners must implement defensive measures like encryption, session management, and advanced network monitoring. Awareness of these threats and how to counteract them is crucial in today’s interconnected world.

“The road to success is never easy, but every step forward, no matter how small, brings you closer to your goals. Stay focused, believe in yourself, and embrace the challenges along the way for they are the stepping stones to your greatness.”