In Android development, UI Components (User Interface Components) are the building blocks of your app’s screen. Every visible element like a button, text field, or image is a part of the app’s UI.
These components are defined in XML layout files and connected to your logic using Java or Kotlin in your Activity files.
Common UI Components in Android
Let’s look at the most commonly used UI elements.
Button
A Button is a clickable component that performs an action when pressed.
Example:
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSubmit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Submit" />Java/Kotlin:
Button btn = findViewById(R.id.btnSubmit);
btn.setOnClickListener(v -> {
Toast.makeText(this, "Button Clicked!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
});
TextView
A TextView displays text to the user.
Example:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvMessage"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:textColor="@color/black" />Use Case:
Show messages, titles, labels, or any static text.
EditText
An EditText allows users to type text input like entering their name or email.
Example:
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etName"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter your name" />Getting Input in Java/Kotlin:
EditText etName = findViewById(R.id.etName);
String userName = etName.getText().toString();
ImageView
An ImageView displays images such as logos or photos.
Example:
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imgLogo"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:src="@drawable/logo" />You can change the image dynamically:
imgLogo.setImageResource(R.drawable.profile_picture);Event Handling in Android
Event handling means responding to user interactions like button clicks, text input, or swipes. Android provides listeners that “listen” for these actions.
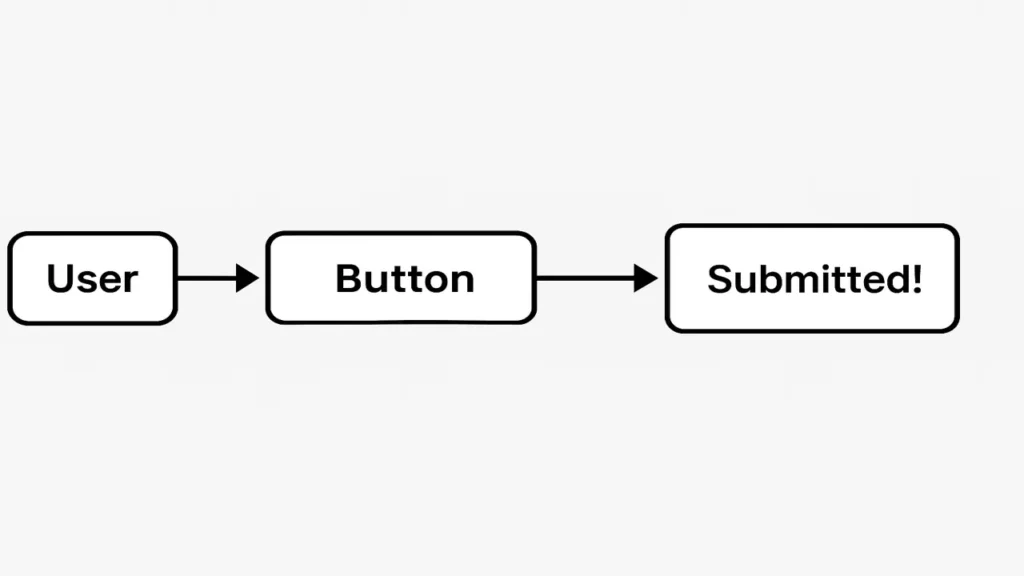
Click Listeners
When a user taps a button or image, a Click Listener detects it.
Example:
Button btnSubmit = findViewById(R.id.btnSubmit);
btnSubmit.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Submitted!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
Toast Messages
A Toast is a short pop-up message that appears briefly on the screen.
Example:
Toast.makeText(this, "Data Saved Successfully!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();Snackbars
Snackbars are similar to Toasts but can include actions (e.g., “Undo”).
Example:
Snackbar.make(view, "Item Deleted", Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG)
.setAction("UNDO", v -> {
// Undo code here
})
.show();Handling User Input
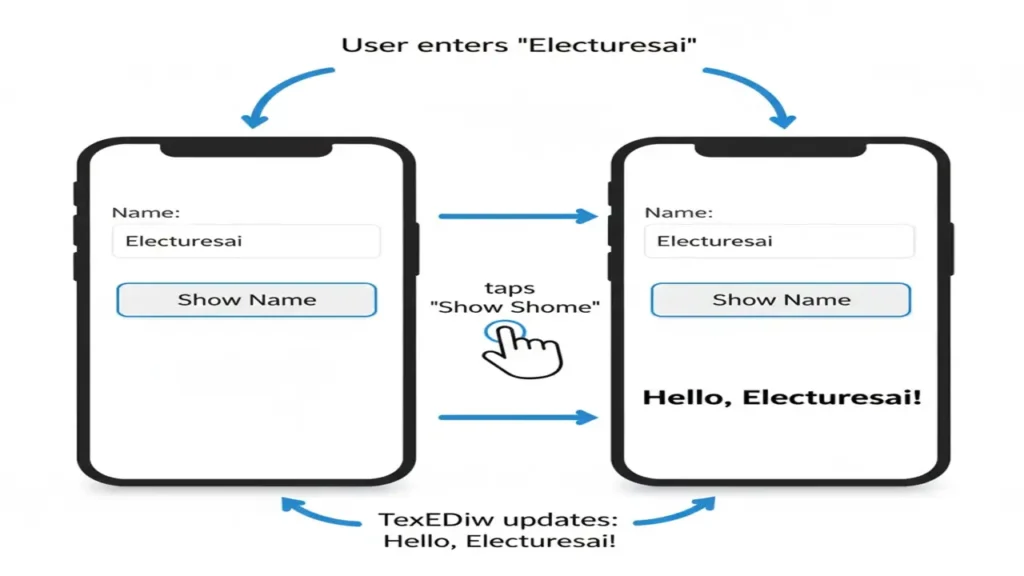
Combining EditText and Button, we can create a simple user interaction.
Example App: Display name after button click.
XML Layout:
<EditText
android:id="@+id/etName"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter your name" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnShow"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Show Name" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvResult"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="" />Java/Kotlin Code:
EditText etName = findViewById(R.id.etName);
TextView tvResult = findViewById(R.id.tvResult);
Button btnShow = findViewById(R.id.btnShow);
btnShow.setOnClickListener(v -> {
String name = etName.getText().toString();
tvResult.setText("Hello, " + name + "!");
});
Summary and Learning Outcome
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Button | Performs action when clicked | “Submit” button |
| TextView | Displays static or dynamic text | “Welcome” label |
| EditText | Takes user input | “Enter Name” field |
| ImageView | Shows an image resource | App logo |
| Click Listener | Handles click events | setOnClickListener() |
| Toast / Snackbar | Shows quick user messages | “Saved!”, “Undo” |
Concluding Thoughts
- Design Android UIs using Buttons, TextViews, EditTexts, and ImageViews
- Handle events with Click Listeners
- Provide user feedback using Toasts and Snackbars
- Build interactive input-based mini-apps
Suggested Practice
- Create a login screen with two EditTexts (username, password) and a login button.
- Show a Toast message “Login Successful!” after clicking the button.
- Add a reset button that clears the text fields.
People also ask:
UI components are reusable elements like buttons, input fields, sliders, and menus that help build consistent and interactive user interfaces.
Event handling lets applications respond to user actions like clicks or key presses, making the interface dynamic and interactive.
In event bubbling, events move from the target element up to its ancestors, while in capturing, they move from ancestors down to the target.