Present rapid warming shows Earth is heating faster than ever recorded. Learn how scientists project future climate change and why uncertainty in climate projections matters for understanding our planet’s future.
Introduction
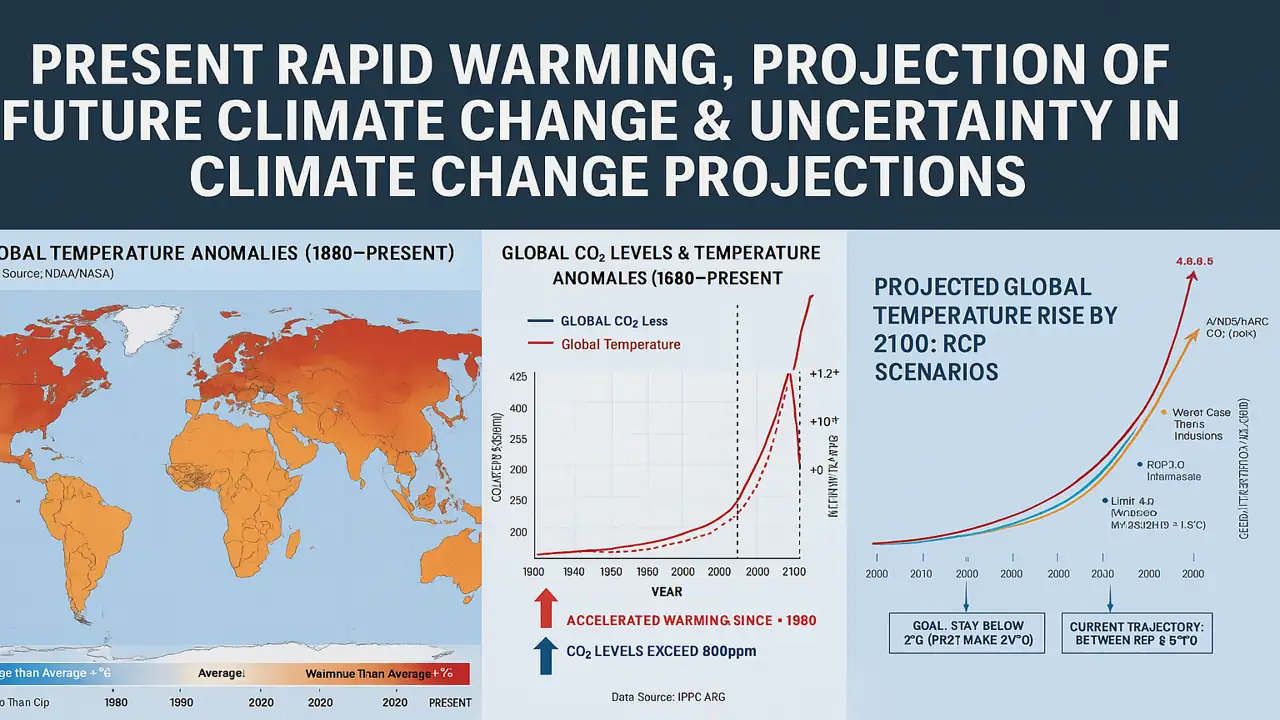
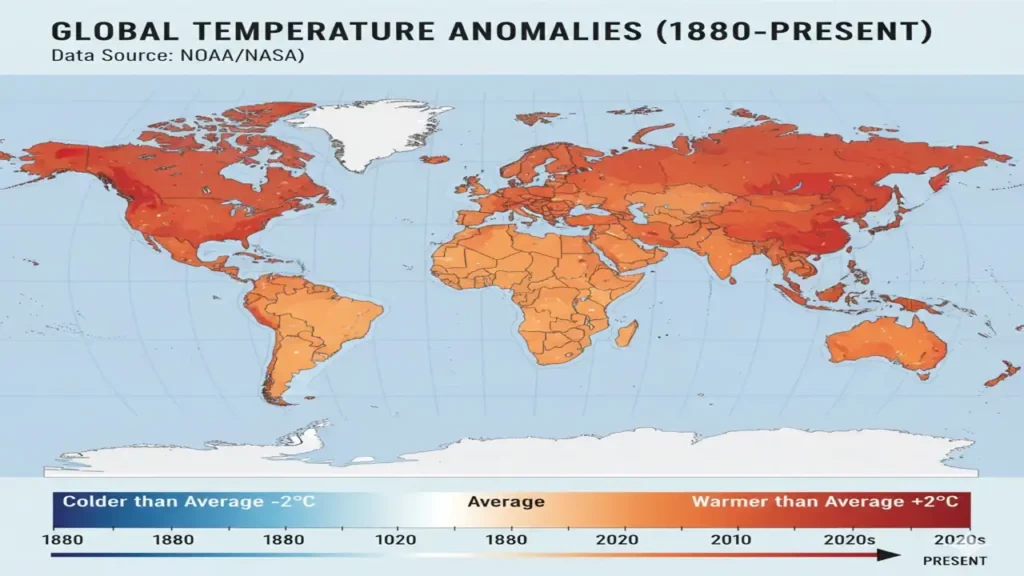
Earth’s climate is warming at an unprecedented pace. Over the past century, global average temperatures have risen by more than 1.1 °C and two-thirds of that warming has occurred since 1975.
The signs are everywhere: record-breaking heatwaves, melting glaciers, stronger storms, and longer droughts. Human activity burning fossil fuels and deforestation has pushed greenhouse gas levels to heights not seen in 3 million years.
Present Rapid Warming The Evidence
Modern technology allows scientists to measure warming across land, sea, and atmosphere.
With rapid warming there are also some impacts on climate change, you must to know.
Key Indicators of Current Warming
- Surface Temperature Rise:
Each of the last eight years has been the warmest on record. - Ocean Heat Content:
The oceans absorb 90% of excess heat causing thermal expansion and sea-level rise. - Cryosphere Changes:
Arctic sea ice has shrunk by over 40% since the 1980s. - Greenhouse Gas Concentration:
CO₂ levels surpassed 420 ppm in 2024 a record high.
This rapid warming is unequivocally linked to anthropogenic activity.
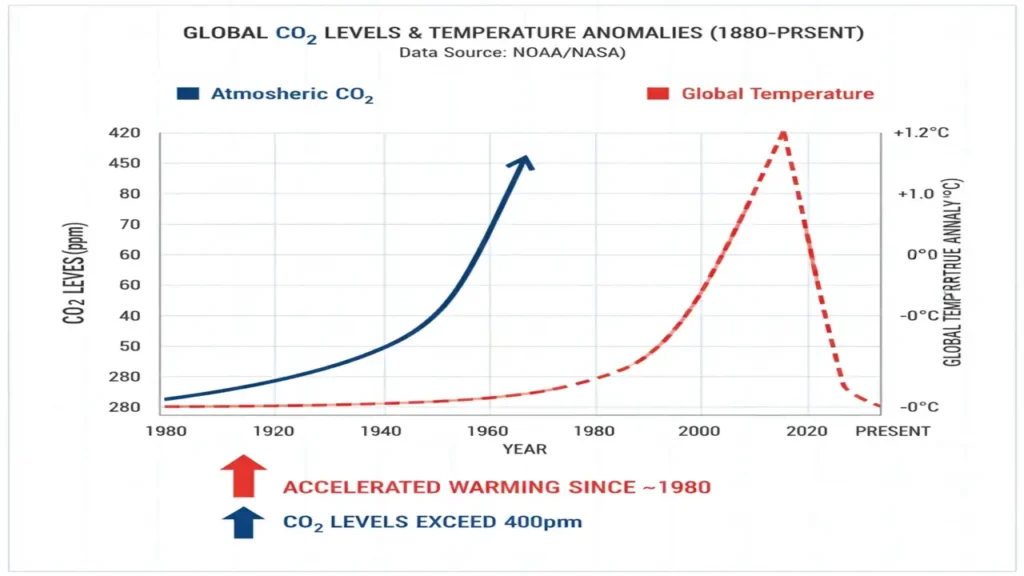
Projection of Future Climate Change
Climate scientists use sophisticated models to simulate how Earth’s climate may change over the next century.
These General Circulation Models (GCMs) combine atmospheric physics, ocean currents, and land processes to create scenarios known as RCPs (Representative Concentration Pathways) or SSPs (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways).
Future Projections by 2100
- RCP 2.6 (Low Emissions): Warming limited to ~1.5 °C with aggressive mitigation.
- RCP 4.5 (Moderate): 2–3 °C increase with partial reduction in emissions.
- RCP 8.5 (High Emissions): 3.5–5 °C rise if fossil fuel use continues unchecked.
These projections illustrate how choices made today define our climate tomorrow.
Uncertainty in Climate Change Projections
Climate projections are scientifically rigorous but carry degrees of uncertainty.
This does not mean they are unreliable it means scientists account for the complexity of the Earth system.
Sources of Uncertainty
- Natural Variability: Volcanic eruptions, solar cycles, and ocean currents can temporarily alter trends.
- Emission Pathways: Future human choices in energy and policy are impossible to predict exactly.
- Model Differences: Each model handles cloud feedback, aerosols, and ice dynamics slightly differently.
Despite these uncertainties, the direction is clear continued emissions mean continued warming.
Reactions and Attitudes to Climate Change
Conclusion
The science of climate projections does not aim to predict the exact temperature of a single day in 2100.
Instead, it gives us a map of possibilities each dependent on our actions now.
The present rapid warming is undeniable; future warming is avoidable. With science-driven policy, green technology, and global cooperation, we can reshape the projections toward a stable planet.
People also ask:
It refers to the unusually fast rise in global temperatures over the past century, mainly caused by human activities like burning fossil fuels.
Because greenhouse gas emissions from industries, vehicles, and deforestation have sharply increased, trapping more heat in the atmosphere.
It leads to more extreme weather, melting ice, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems and human livelihoods.