Eutrophication, sewage sludge treatment, polluted water remediation, and thermal pollution causes and control, with real examples from Pakistan’s environment.
Control Remediation
Definition:
The process of treating and restoring polluted environments (soil or water) through physical, chemical, or biological means.
Major Remediation Techniques:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Removal or isolation of pollutants | Filtration, sedimentation tanks |
| Chemical | Adding reagents to neutralize contaminants | Chlorination, coagulation, oxidation |
| Biological | Microbes degrade pollutants | Bioreactors, wetlands |
| Phytoremediation | Plants absorb or detoxify pollutants | Water hyacinth removing heavy metals |
Pakistan Example:
In Faisalabad textile industry, chemical treatment units neutralize dyes before wastewater discharge.
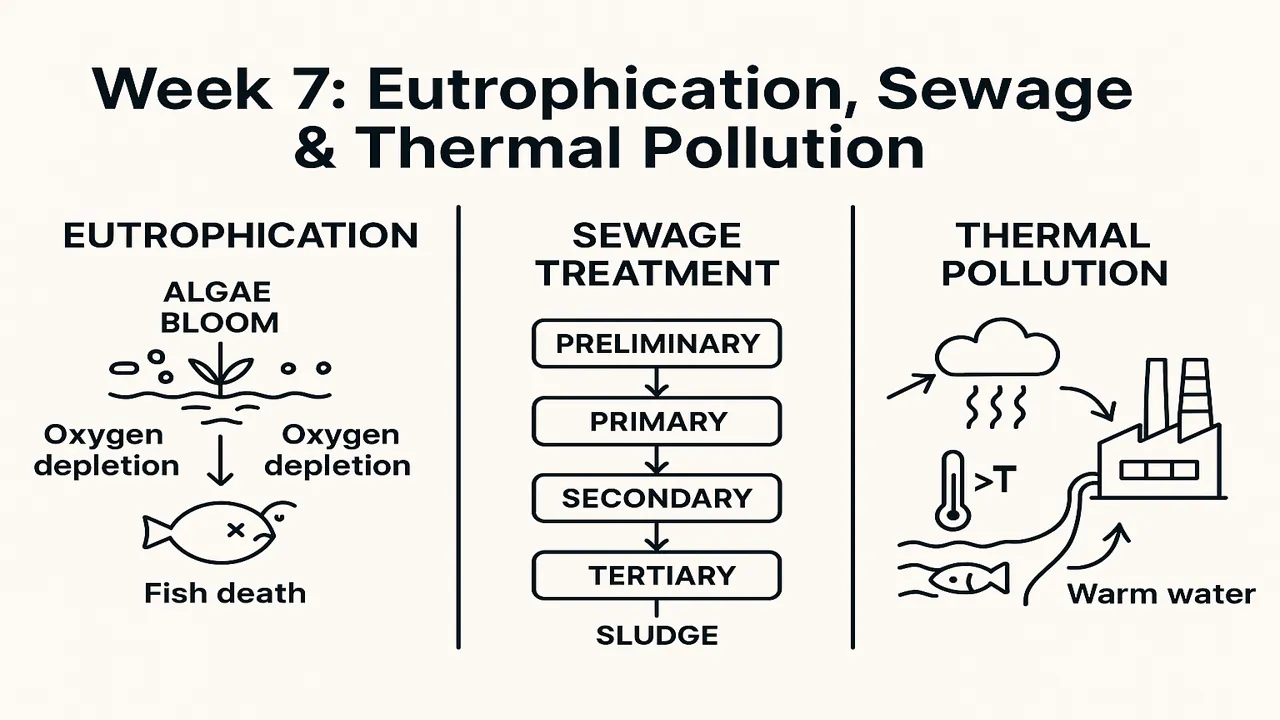
Eutrophication
Definition:
Eutrophication is the enrichment of water bodies with nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) leading to excessive algal growth.
Process:
- Fertilizer runoff or sewage introduces nutrients into lakes or rivers.
- Algae bloom covers water surface, blocking sunlight.
- Algae die and decompose, consuming oxygen (↓DO).
- Aquatic animals suffocate → fish kills.
Results:
- Oxygen depletion (hypoxia).
- Biodiversity loss.
- Foul smell and taste in water.
- Toxic algal blooms (cyanobacteria).
Pakistan Examples:
- Rawal Lake, Islamabad: eutrophication from nearby settlements and agricultural runoff.
- Manchar Lake, Sindh: nutrient loading from fertilizers and wastewater.
Control:
- Reduce fertilizer use.
- Treat sewage before discharge.
- Encourage buffer strips near farms.
- Apply biomanipulation (use of grazing fish to control algae).
Sewage and Sludge Treatment
Objective: To remove contaminants from domestic and industrial wastewater before it’s released back into the environment.
Steps in Sewage Treatment
- Preliminary Treatment: Screens remove large solids.
- Primary Treatment: Sedimentation tanks allow solids to settle.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological oxidation (activated sludge, trickling filters).
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced filtration, chemical disinfection, nutrient removal.
- Sludge Treatment: Thickening → Digestion (anaerobic) → Dewatering → Disposal or composting.
Pakistan Examples:
- Lahore’s Shadbagh & Gulshan-e-Ravi plants treat municipal wastewater.
- Karachi’s TP-III treatment plant treats industrial + domestic effluent using biological methods.
Reuse Option:
- Treated water can irrigate non-edible crops.
- Sludge can be composted for soil enrichment.
Thermal Pollution
Definition:
The increase in natural water temperature due to discharge of heated effluents, typically from power plants, factories, or refineries.
Causes:
- Cooling water from thermal and nuclear plants.
- Industrial wastewater.
- Deforestation reducing natural shading.
Effects:
- Decreased dissolved oxygen (DO).
- Disruption of aquatic species (fish migration, breeding).
- Increased algal growth.
- Stress on sensitive species (trout, salmon).
Example (Pakistan):
Thermal discharges from Guddu and Muzaffargarh power plants raise canal water temperature, altering aquatic ecology.
Control Measures:
- Cooling ponds and towers.
- Heat exchangers to reuse waste heat.
- Planting vegetation along waterways for shade.
Summary
Week 7 explains how polluted water systems can be rehabilitated through remediation and treatment technologies. Eutrophication and thermal pollution threaten aquatic life but can be controlled through eco-engineering, wastewater treatment, and public awareness.
The approach followed at E Lectures reflects both academic depth and easy-to-understand explanations.
People also ask:
Nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizers and sewage cause algal blooms.
Yes, for irrigation, industrial cooling, or groundwater recharge.
It reduces oxygen and disturbs reproductive cycles of fish.
Biogas (methane + CO₂) which can be used as an energy source.
They act as natural biofilters, removing nutrients and heavy metals.