Soil pollution and its impacts, major sources, types of contaminants, and sustainable control methods with Pakistan-focused examples.
Introduction to Soil Pollution
Definition:
Soil pollution is the contamination of the soil environment by toxic chemicals or waste materials, reducing soil fertility and threatening life.
Key Concept:
Pollutants accumulate in soil faster than they can be broken down → leading to long-term environmental damage.
Major Sources of Soil Pollution
| Source | Description | Common Pollutants | Example (Pakistan) |
|---|---|---|---|
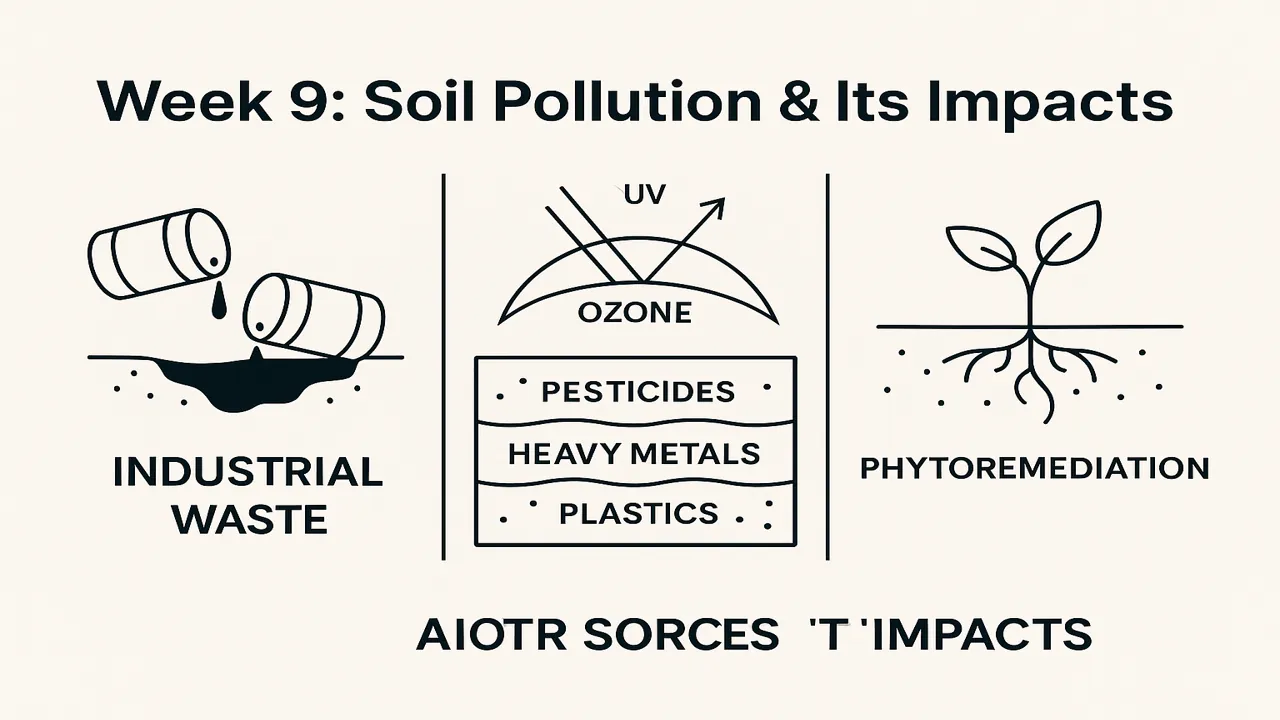
| Industrial Waste | Improper disposal of chemicals and heavy metals | Lead, arsenic, cadmium, chromium | Tanneries in Kasur, factories in Karachi SITE area |
| Agricultural Activities | Excess fertilizer, pesticide, and herbicide use | Nitrates, phosphates, DDT, organophosphates | Cotton fields of Multan & Bahawalpur |
| Urban Waste | Open dumping of garbage, plastics, e-waste | Microplastics, toxic residues, batteries | Lahore suburban dumps |
| Mining and Quarrying | Extraction exposes heavy metals | Mercury, sulfur, acid mine drainage | Khewra salt mines (residual contamination) |
| Oil & Hydrocarbons | Spills during transport or storage | Crude oil, lubricants, PAHs | Attock refinery and transport routes |
Types of Soil Pollutants
- Organic Pollutants:
- Pesticides, hydrocarbons, plastics, detergents
- Persistent in environment (e.g., DDT, PCBs).
- Inorganic Pollutants:
- Heavy metals (lead, mercury, cadmium, zinc).
- Toxic even at low concentrations.
- Biological Pollutants:
- Pathogens from sewage or animal waste.
- Cause diseases in humans and livestock.
- Radioactive Pollutants:
- From nuclear waste, improper medical disposal.
- Long-term radiation effects.
Impacts of Soil Pollution
On Environment:
- Reduced fertility → lower crop yield.
- Acidification and loss of organic matter.
- Disturbed microbial balance.
- Contaminated groundwater (leaching).
On Human Health:
- Heavy metals cause cancer, nerve, and kidney diseases.
- Pesticide residues linked to hormonal disorders.
- Pathogen-laden soil spreads infections.
Pakistan Examples:
- Kasur: chromium contamination from tanneries.
- Multan: pesticide accumulation in cotton soils.
- Karachi Malir: heavy-metal-laden urban soils from industries.
Week 8 – Agricultural Pollution, Greenhouse Effect, Global Warming, Ozone Depletion and Its Effects
Control and Remediation Measures
- Soil Testing & Monitoring: Regular evaluation of heavy metals and pH.
- Phytoremediation: Using plants like sunflower and mustard to absorb toxins.
- Bioremediation: Employing microbes to degrade organic pollutants.
- Use of Organic Fertilizers: Compost, green manure.
- Legislation: Implementation of Pakistan Environmental Protection Act (PEPA, 1997).
- Public Awareness: Proper disposal of agrochemical containers and waste.
Summary
Week 9 focuses on soil pollution and its impacts, linking agricultural misuse, industrial dumping, and urban expansion to declining soil health. Sustainable farming, eco-remediation, and strong regulation are key to restoration.
The approach followed at E Lectures reflects both academic depth and easy-to-understand explanations.
People also ask:
Industrial effluents and excessive use of agrochemicals are the top causes.
They kill not only pests but also beneficial organisms, and remain in the soil for years.
Certain plants absorb or break down toxins this is called phytoremediation.
Lead, cadmium, mercury, and chromium.
By using organic fertilizers, rotating crops, and minimizing pesticide use.