Introduction
Neural Networks basics form the foundation of modern Deep Learning systems. They are computational models inspired by the human brain and are widely used in computer vision, NLP, speech processing, and generative AI. Understanding neural networks basics is essential before moving toward advanced topics like activation functions, loss functions, backpropagation, and optimization algorithms.
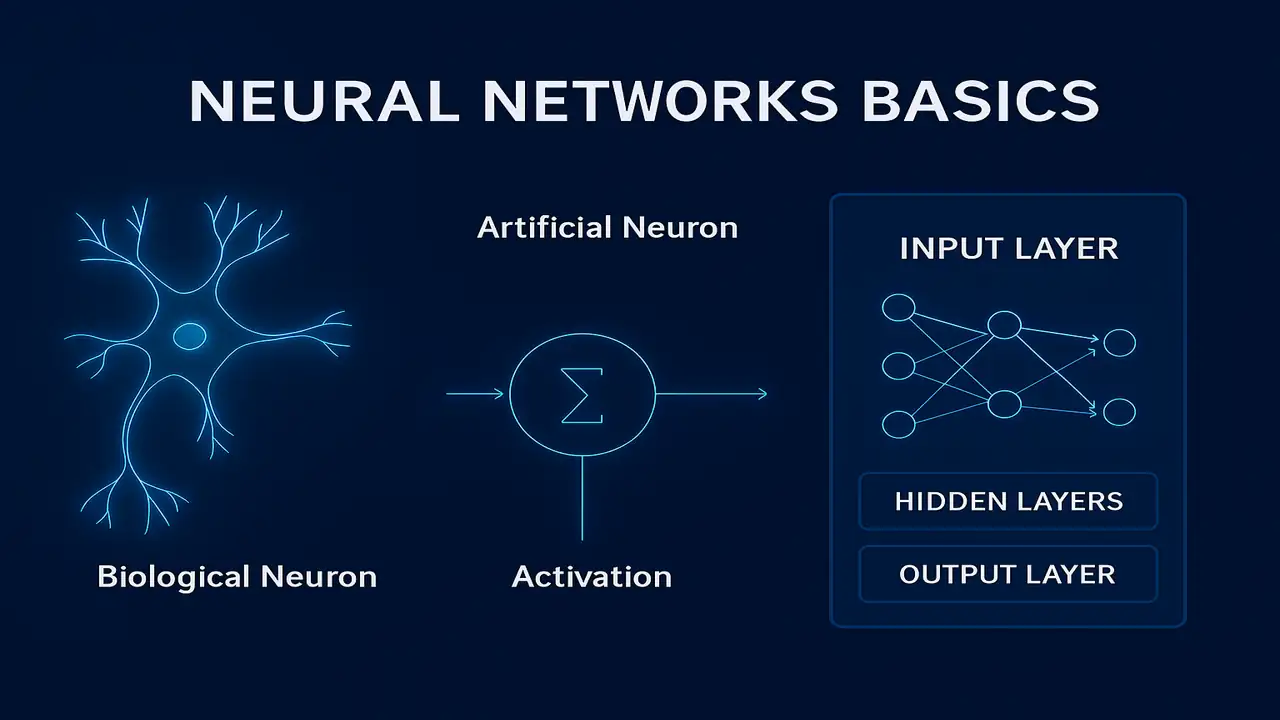
Biological Neuron vs Artificial Neuron
A biological neuron consists of:
- Dendrites → receive signals
- Cell body (soma) → processes the signal
- Axon → sends output to other neurons
The artificial equivalent is modeled as: y=f(w1x1+w2x2+…+b)
Where:
- x = inputs
- w = weights
- b = bias
- f = activation function
This representation enables neural networks to learn patterns from datasets.
Architecture of a Neural Network
A neural network typically has three types of layers:
1. Input Layer
Receives raw input data (images, text, numeric features).
2. Hidden Layers
Performs transformations to extract patterns.
More hidden layers → Deep Neural Network (DNN).
3. Output Layer
Generates predictions such as classification probabilities or numeric values.
How a Neuron Computes Output (Step-by-Step)
Let’s take a simple example:
Inputs:
x₁ = 2
x₂ = 3
Weights:
w₁ = 0.4
w₂ = 0.6
Bias:
b = 0.2
Step 1 – Weighted Sum
z=(2×0.4)+(3×0.6)+0.2=0.8+1.8+0.2=2.8
Step 2 – Activation Function
Assume ReLU: y=max(0,z)=2.8
This is how neural networks process information layer-by-layer.
Types of Neural Networks (High ranking section)
1. Feedforward Neural Network (FNN)
Simplest type. Data flows only forward.
2. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Best for images, video, medical scans.
3. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
Used for sequences such as text and speech.
4. Transformer Architecture
Modern, powerful architecture used by ChatGPT and BERT.
Forward Propagation (Simplified)
- Input flows into the first layer
- Weighted sums are calculated
- Activation functions transform outputs
- Data passes to the next layer
Why Neural Networks Work So Well?
- Learn hierarchical features
- Non-linear transformations
- Scalable with GPU hardware
- Suitable for large datasets
- Excellent for unstructured data
Lecture 1 – Introduction to Deep Learning: Concepts, Architecture & Applications (2025 Guide)
Summary
Neural networks are the centerpiece of deep learning. Their layered architecture, ability to learn complex representations, and scalability make them indispensable in AI. Understanding neural network components and computations prepares students for deeper topics like activation functions, backpropagation, and optimization algorithms in the upcoming lectures.
People also ask:
A computational model inspired by the human brain that learns from data using layers of interconnected neurons.
Weights, biases, neurons, layers, activation functions, and loss functions.
They introduce non-linearity and help the network learn complex patterns.
A network where data flows only in one direction from input to output.
ChatGPT uses the Transformer architecture, a modern variant of deep neural networks.