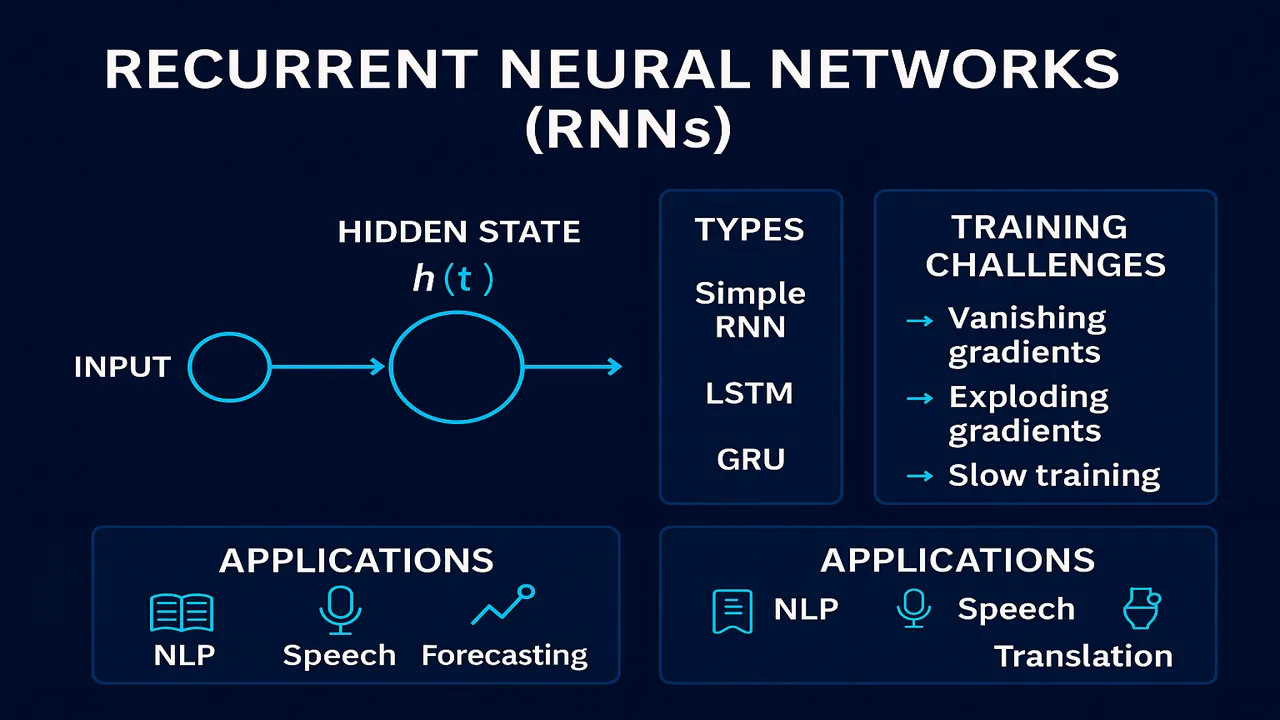
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are, how they handle sequence data, their internal architecture, types (Simple RNN, LSTM, GRU), training challenges, and real-world applications such as NLP, speech recognition, and time-series forecasting.
Introduction to RNNs
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a powerful deep-learning architecture designed specifically for sequential or time-dependent data. Unlike feed-forward networks, RNNs have loops that allow information to persist across steps.
This makes them suitable for tasks like:
- Language modeling
- Text generation
- Speech recognition
- Time-series prediction
- Machine translation
Why Do We Need RNNs?
Traditional neural networks treat inputs independently.
But many real-world tasks require understanding context:
- A sentence depends on previous words.
- Stock prices depend on previous movements.
- Audio signals depend on earlier waves.
RNNs solve this by introducing memory through recurrent connections.
RNN Architecture (Simple RNN)
A simple RNN accepts input at each time step t and passes information forward through a hidden state:
Formula
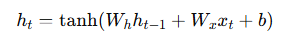
Where:
- Xt: Input at time step t
- ht: Hidden state
- ht−1: Previous memory
- Wh,Wx: Weight matrices
- tanh: Activation
- b: Bias
Great for explaining why GRU is simpler than LSTM.
🔗 https://deepmind.com/research
Types of RNNs
A) Simple RNN
- Basic model
- Suffers from vanishing gradients
- Short-term memory only
B) Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
Designed to learn long-term dependencies using:
- Input gate
- Forget gate
- Output gate
- Cell state
LSTMs solve the vanishing gradient problem and are widely used in NLP.
C) Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)
A simplified LSTM with two gates:
- Update gate
- Reset gate
GRUs train faster and often match or outperform LSTMs.
Training Challenges (with Solutions)
| Challenge | Why It Happens | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Vanishing gradient | Gradients become too small | Use LSTM / GRU, ReLU |
| Exploding gradient | Gradients grow uncontrollably | Gradient clipping |
| Slow training | Sequential processing | Use cuDNN-optimized RNNs |
Lecture 9 – Convolution Operations in CNNs: Filters, Kernels & Feature Extraction Explained
Real-World Applications of RNNs
Natural Language Processing
- Text classification
- Chatbots
- Sentiment analysis
Speech Recognition
- Voice assistants
- Transcription
Time Series Forecasting
- Weather prediction
- Stock market trends
Machine Translation
- English → Urdu
- Urdu → Arabic
- Multilingual LLM components
Music Generation
Sequential patterns in melodies.
Example – Predicting Next Word in a Sentence
Input sentence:
“Artificial intelligence is the”
The RNN takes each word sequentially and updates its hidden state.
At the final time step, it predicts the next word.
Output prediction:
“future” (for example)
Summary
Recurrent Neural Networks allow deep learning models to remember previous steps, making them ideal for sequential tasks.
With variants like LSTM and GRU, they overcome limitations of simple RNNs and achieve state-of-the-art performance in NLP, speech, and time-series applications.
People also ask:
RNNs are used for sequence data like text, speech, audio, and time-series.
Because of the vanishing gradient problem, causing them to forget earlier steps.
Both perform well. LSTMs are more powerful; GRUs are faster.
Chatbots, Siri, Google Assistant, stock prediction, machine translation.
Transformers outperform RNNs in NLP but RNNs are still useful for smaller, lightweight models.