Introduction
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) allow models to learn from sequential data text, speech, sensor signals, time-series patterns, and more. But as sequences grow longer, traditional RNNs struggle with vanishing gradients, losing information from earlier time steps. This limitation led to advanced architectures like LSTMs and GRUs (Gated Recurrent Units).
In this lecture, we explore GRUs, one of the most powerful and efficient recurrent architectures in deep learning. GRUs simplify the LSTM design while maintaining competitive performance, reduced training time, and strong accuracy across NLP, forecasting, and sequential learning tasks.
What Are GRUs?
GRUs (Gated Recurrent Units) are a type of recurrent neural network that handle long-term dependencies using gates. These gates control how much past information should be carried forward and how much new information should be added.
Think of GRUs as a simplified version of LSTMs same power, fewer parameters, faster learning.
Why are GRUs important?
- They solve the vanishing gradient problem
- They preserve context over long sequences
- They are computationally efficient
- They perform on par with LSTMs but train faster
- They work especially well with limited training data
GRUs strike a perfect balance between accuracy and efficiency, making them a favorite for real-world deployments.
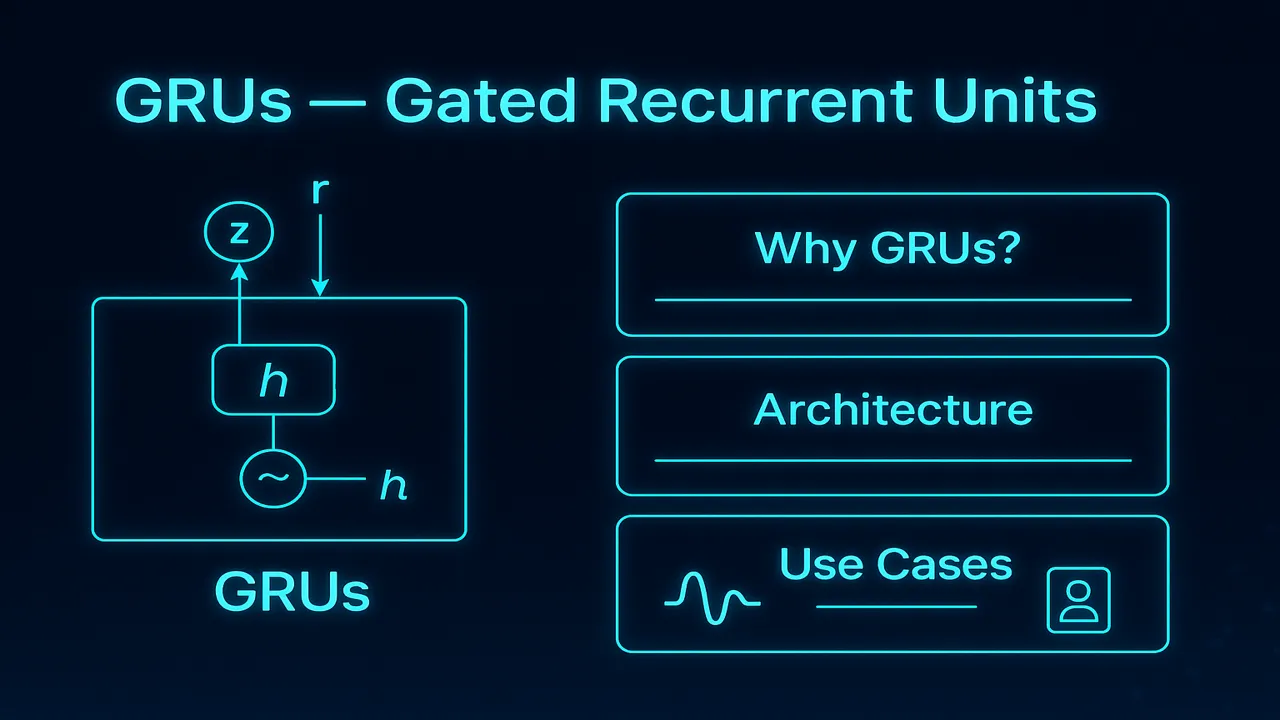
GRU Architecture
Unlike LSTMs which have three gates, GRUs rely on two gates:
- Update Gate (zₜ)
- Reset Gate (rₜ)
GRUs do not maintain a separate cell state like LSTMs. Instead, they directly operate on the hidden state.
Update Gate (zₜ)
The update gate controls how much of the past information should be kept.
Formula:
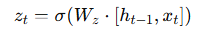
If zt is close to 1 → keep old information.
If zt is close to 0 → update with new information.
Reset Gate (rₜ)
The reset gate decides how much past information to forget.
Formula:
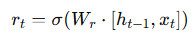
If rt ≈ 0 → ignore previous hidden state.
If rt ≈ 1 → use full history.
Candidate Hidden State (ĥₜ)
After controlling memory with the reset gate, the GRU computes a new hidden representation.
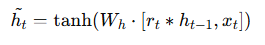
Final Hidden State (hₜ)
The update gate blends old + new information to produce the final output:
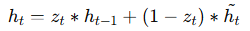
This makes GRUs elegant, intuitive, and highly efficient.
How GRUs Process Information (Step-by-Step Example)
Let’s take a simple sentence:
“The weather is nice today.”
We want the model to predict the next word: sunny.
Step 1 – Convert words to vectors
Each word becomes an embedding:
- “The” → vector
- “weather” → vector
- … until “today”
Step 2 – First hidden state
GRU takes the vector for “The”:
- update gate decides how much previous info to keep (initially none)
- reset gate is high → model uses full info
- hidden state is initialized
Step 3 – Process next word
For word “weather”:
- update gate checks: “Is old info important?”
- reset gate: “Do we need to forget older context?”
- new candidate hidden state created
- final hidden state computed
Step 4 – Continue through sequence
Each word updates the hidden state.
Step 5 – Prediction
At the final step:
Model predicts “sunny” because GRU preserved the pattern
weather → nice → today → sunny
This illustrates the GRU power: long-term consistency without computational overhead.
Lecture 11 – LSTM Networks in Deep Learning: Architecture, Gates & Real-World Applications
GRUs vs LSTMs Which Is Better?
| Feature | LSTM | GRU |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Gates | 3 (Input, Forget, Output) | 2 (Update, Reset) |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Memory | Larger | Smaller |
| Accuracy | Slightly better for large datasets | Comparable for most tasks |
| Best Use | Complex long-sequence tasks | Real-time / small-data tasks |
Summary:
- Training Efficiency → GRU Wins
- Simplicity → GRU Wins
- Long-range accuracy → LSTM Slightly Wins
- Most real-world applications → GRU performs equally well
Why GRUs Train Faster?
GRUs eliminate:
- Output gate
- Separate cell state
- Extra matrix multiplications
This reduces total parameters by 30–40%.
This makes GRUs ideal for:
- Mobile apps
- Embedded AI systems
- Low-power devices
- Real-time NLP
- Startups with limited compute
Applications of GRUs
Natural Language Processing
- Chatbots
- Translation
- Sentiment analysis
- Autocomplete
- Text generation
Speech Recognition
GRUs handle audio frames smoothly due to efficient sequential modeling.
Time-Series Forecasting
- Stock predictions
- Weather forecasting
- Sales forecasting
- Energy demand prediction
Anomaly Detection
GRUs detect unusual patterns in:
- Network traffic
- Financial activity
- Sensor readings
Healthcare
- ECG pattern learning
- Patient vitals monitoring
- Early disease detection
Robotics
- Sensor fusion
- Trajectory prediction
GRUs are used everywhere sequential predictions matter.
GRU Training Tips (For High Accuracy)
Tip 1 – Use Dropout
GRUs may overfit due to strong memory.
Tip 2 – Use Bidirectional GRUs
Captures past + future context.
Tip 3 – Use Layer Normalization
Improves gradient flow.
Tip 4 – Combine GRUs with CNN Features
Excellent for NLP, audio, and multimodal tasks.
Tip 5 – Tune Learning Rate
GRUs are sensitive to high learning rates.
Summary
Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) are powerful RNN variants designed to solve long-term dependency issues while keeping the architecture simple and efficient. With only two gates (reset + update), GRUs train faster, use fewer parameters, and perform extremely well on sequential tasks such as NLP, time-series forecasting, and speech processing.
GRUs offer nearly the same power as LSTMs but with better speed making them an excellent choice for real-world applications, especially where compute is limited.
People also ask:
For most tasks, yes GRUs train faster and perform similarly. For very long sequences, LSTMs may have a slight edge.
To simplify learning and reduce parameters. Fewer gates = faster training.
Much less than standard RNNs. GRUs manage memory efficiently using the update gate.
NLP, forecasting, anomaly detection, speech recognition, and healthcare predictions.
GRUs often outperform LSTMs on small datasets due to fewer parameters.