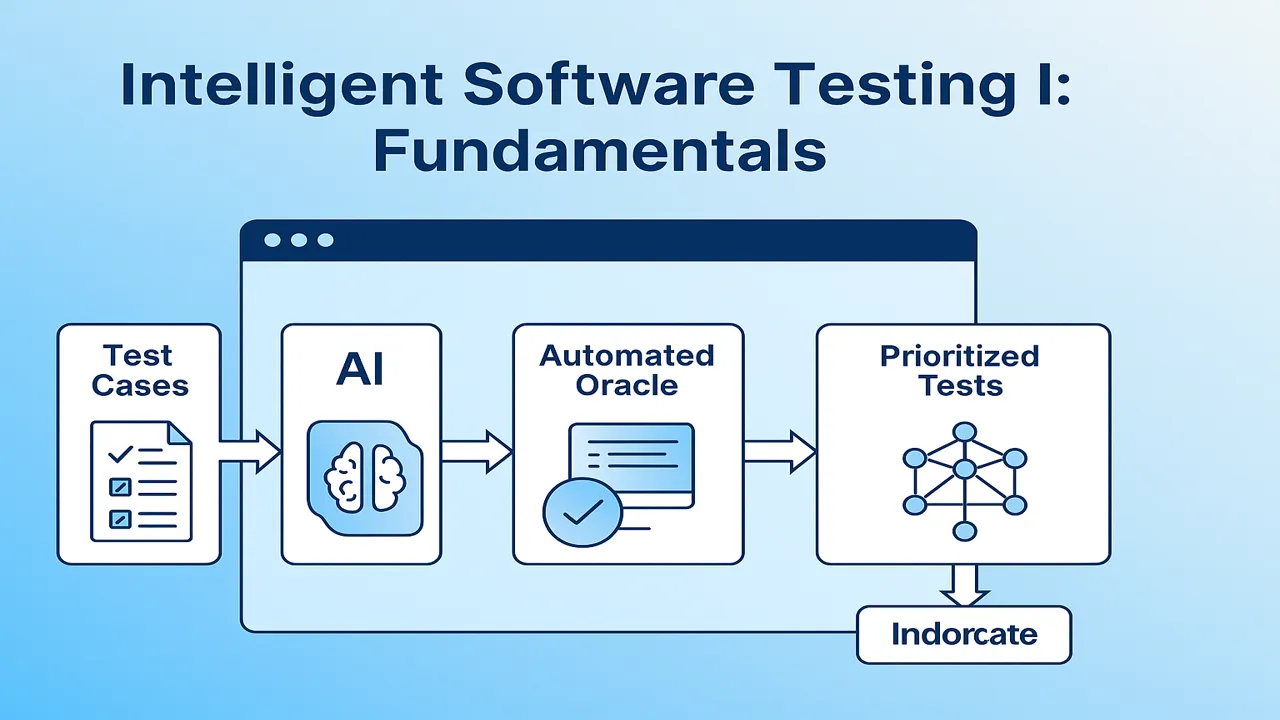
Explore Intelligent Software Testing fundamentals: AI-driven test generation, automated oracle solutions, and ML-based test prioritization for efficient QA.
Software testing is a crucial part of the SDLC, ensuring quality, reliability, and correctness. Modern intelligent systems leverage AI and ML to automate and optimize testing processes, reducing manual effort and improving coverage.
Introduction
Software testing is a critical phase in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Traditional testing methods, while effective, often require extensive manual effort, time, and resources. As software systems grow more complex, ensuring quality, reliability, and correctness becomes increasingly challenging.
Enter Intelligent Software Testing (IST) a paradigm that leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to automate, optimize, and predict testing processes. IST does not replace human engineers but augments their capabilities, enabling faster, smarter, and more reliable testing.
In this week’s lecture, we explore three core components of Intelligent Software Testing:
- Test Case Generation using AI
- Automated Oracle Problem
- Test Prioritization and Selection using ML
These components form the foundation for building efficient and adaptive testing pipelines that can handle modern software challenges.
Test Case Generation Using AI
Generating test cases is often one of the most time-consuming aspects of QA. Developers manually write test cases based on requirements and code logic, but this approach can miss edge cases or fail to cover unexpected input scenarios.
How AI Helps
AI-powered test generation tools automate this process using search-based software engineering (SBSE) techniques:
- Optimization Algorithms: Search-based approaches, like genetic algorithms and simulated annealing, generate test inputs that maximize code coverage and detect faults.
- Intelligent Test Suites: AI analyzes requirements and source code to generate high-coverage test cases automatically.
- Scenario Simulation: AI simulates diverse input combinations, identifying potential edge cases that might be missed manually.
Example:
Consider a payment module for an e-commerce application. AI can generate thousands of input scenarios (valid, invalid, boundary, and edge cases) to ensure the module handles all possible transaction scenarios without failure.
Benefits of AI Test Generation
- Time Efficiency: Reduces manual test case writing.
- Enhanced Coverage: Finds edge cases human testers may overlook.
- Consistency: Maintains standard test quality across iterations.
- Continuous Learning: AI improves test generation over time using historical data.
Automated Oracle Problem
In software testing, an oracle determines whether a program’s output is correct for a given input. Traditional oracles require hard-coded expected outputs or human verification, which is not scalable for complex systems.
AI-Powered Oracle Solutions
AI introduces automated oracle systems capable of predicting expected outputs and detecting anomalies:
- ML Prediction: Models predict expected outputs for new inputs based on historical data or program specifications.
- Deviation Detection: Compares actual vs predicted outputs to identify inconsistencies.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Engineers no longer need to manually specify expected results for every test case.
Example:
For an online banking system, an AI oracle can automatically verify that a funds transfer produces correct balances, flags suspicious outputs, and alerts developers to potential errors.
Advantages of AI Oracles
- Automation: Reduces human oversight in verification.
- Speed: Real-time validation for large-scale systems.
- Accuracy: Detects subtle bugs or unexpected behaviors.
- Adaptability: Can adjust predictions as software evolves.
Test Prioritization and Selection Using ML
Regression testing ensures that new code changes do not break existing functionality. In large systems, running all tests for every change is inefficient. ML helps prioritize and select the most important test cases.
How ML Enhances Regression Testing
- Risk Assessment: ML models analyze code changes and predict high-risk modules that require more thorough testing.
- Test Selection: Only the most relevant test cases are executed, reducing unnecessary tests.
- Historical Analysis: Past test results and defect patterns guide the prioritization process.
Example:
After a software update, ML identifies that a module handling user authentication has the highest risk and prioritizes associated test cases, while low-risk modules receive lower priority.
Benefits of ML-Based Prioritization
- Faster Testing Cycles: Reduces overall regression testing time.
- Resource Optimization: Focuses QA resources on critical areas.
- Increased Reliability: Detects high-risk defects early.
- Predictive QA: Improves over time as ML models learn from new data.
Integrating AI in Software Testing Pipelines
Intelligent Software Testing is most effective when fully integrated into the CI/CD pipeline:
- Continuous Test Generation: AI generates new test cases as code changes.
- Automated Oracle Verification: Every output is automatically validated.
- ML Test Prioritization: Regression tests are intelligently scheduled.
- Feedback Loop: Test results are fed back into the AI models for continuous improvement.
This approach ensures faster releases, fewer defects, and higher-quality software without increasing human effort.
Summary
- AI automates test case generation, improving coverage and efficiency.
- Automated oracles allow real-time verification without manually defined outputs.
- ML models prioritize and select regression tests, focusing on high-risk modules.
- Integrating these tools into pipelines ensures smarter, faster, and adaptive QA.
Core Insight: In Intelligent Software Engineering, AI doesn’t just assist it actively predicts, verifies, and optimizes software quality across the development lifecycle.