Lecture 13 provides a complete guide to Deep Learning for Data Mining, covering neural network foundations, CNNs, RNNs, LSTMs, Autoencoders, feature learning, backpropagation, training techniques, real-world applications, and case studies.
Deep Learning represents one of the most powerful and transformative advancements in modern Data Mining. Unlike traditional machine learning models that rely heavily on handcrafted features, Deep Learning automatically learns patterns, features, and relationships from raw data. Whether it is images, text, audio, time-series, or sensor logs deep neural networks excel at understanding high-dimensional, complex datasets.
In this lecture, students will understand the architecture, functioning, and practical applications of deep learning models that now power global technology platforms.
Introduction to Deep Learning
Why Deep Learning is Transforming Data Mining
Deep Learning has changed Data Mining because it can:
- Learn features automatically
- Handle massive datasets
- Process raw data directly
- Capture non-linear relationships
Unlike traditional ML (SVM, Decision Trees, Naive Bayes), Deep Learning works exceptionally well for:
- Image mining
- Speech mining
- Text mining
- Video analysis
- IoT sensor data
- High-dimensional data
Traditional ML vs Deep Learning
| Feature | Traditional ML | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Extraction | Manual | Automatic |
| High-Dimensional Data | Poor performance | Excellent |
| Scalability | Medium | High |
| Accuracy | Good | Highest |
| Computation | Less | GPU-intensive |
Biological Inspiration
Deep Learning is inspired by the brain.
Artificial Neurons
A neuron receives input, multiplies by weights, adds bias, and passes through activation.
Formula:
y = activation(Wx + b)Neural Network Layers
Text Diagram:
Input → [Hidden Layer 1] → [Hidden Layer 2] → OutputTypes of layers:
- Dense
- Convolutional
- Recurrent
- Pooling
- Normalization
Lecture 12 – Data Warehousing and OLAP for Data Mining
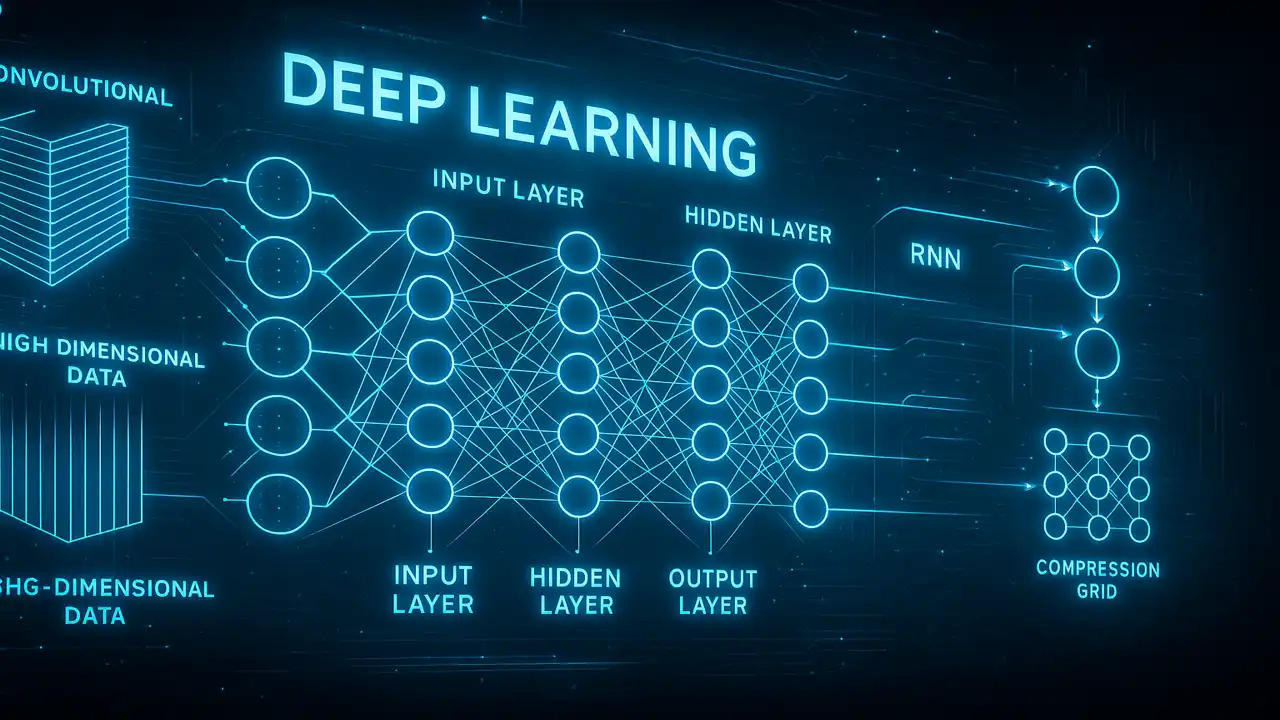
Deep Neural Network Architecture
Input Layer
Receives raw data:
- Pixels
- Words
- Numbers
Hidden Layers
Learn patterns and representations.
Activation Functions
Popular activations:
- ReLU
- Sigmoid
- Tanh
- Softmax
Output Layer
Depends on task:
- Softmax → classification
- Sigmoid → binary classification
- Linear → regression
Gradient Descent & Backpropagation
Loss Functions
Used to measure model error.
Examples:
- Cross-entropy
- MSE
Optimization Algorithms
- Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
- Adam
- RMSProp
Deep Learning Models for Data Mining
1. Multilayer Perceptron (MLP)
Good for:
- Tabular data
- Simple classification
- Regression
2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs use filters to extract patterns.
Used for:
- Image mining
- Video analysis
- Document classification
CNN Diagram:
Image → Convolution → ReLU → Pooling → Dense → Output3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Good for sequential patterns.
Used for:
- Time-series
- Text sequences
- Speech signals
4. LSTMs & GRUs
Fix RNN limitations by solving vanishing gradients.
Used for:
- Long sequences
- Language modeling
- Medical time-series
5. Autoencoders
Used for:
- Dimensionality reduction
- Anomaly detection
- Noise removal
Diagram:
Input → Encoder → Bottleneck → Decoder → ReconstructionFeature Learning & Representation Learning
Why Deep Learning Learns Features Automatically
Because layers stack transformations.
Example:
Image classification:
- Layer 1 → edges
- Layer 2 → textures
- Layer 3 → shapes
- Layer 4 → objects
Embeddings
Vector representations for:
- Words
- Items
- Users
- Nodes in graphs
Used in:
- Recommendation systems
- NLP
Training Deep Learning Models
Data Preparation
Steps:
- Clean data
- Normalize
- Split into training/testing
- Create batches
Regularization
Prevent model overfitting.
Techniques:
- Dropout
- L2 regularization
- Early stopping
Hyperparameter Tuning
Key hyperparameters:
- Learning rate
- Batch size
- Number of layers
- Number of neurons
- Activation functions
Deep Learning for Large-Scale Data Mining
Big Data + Neural Networks
Large datasets require:
- GPUs
- TPUs
- Distributed training
Distributed Training
Frameworks:
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
- Horovod
- Ray
Applications in Real-World Data Mining
Image-Based Data Mining
Used for:
- Medical imaging
- OCR
- License plate detection
NLP & Text Mining
Models:
- BERT
- GPT
- LSTM networks
Applications:
- Chatbots
- Search engines
- Sentiment analysis
Time-Series Mining
Used for:
- Stock prediction
- Weather forecasting
- IoT sensor analysis
Fraud & Anomaly Detection
Autoencoders + LSTM detect suspicious patterns.
Recommender Systems
Deep learning enhances collaborative filtering using embeddings.
Case Studies
Tech Industry
Google uses CNNs + Transformers for:
- Vision models
- Search ranking
- Speech recognition
Healthcare
Deep Learning helps in:
- Cancer detection
- Disease prediction
- Patient risk analysis
Finance
Used for:
- Fraud detection
- Stock forecasting
- Credit scoring
Summary
Lecture 13 provided a detailed understanding of Deep Learning for Data Mining. Students learned neural network foundations, CNNs, RNNs, LSTMs, Autoencoders, feature learning, model training, real-world applications, and case studies. Deep learning now drives nearly all modern AI systems and significantly enhances data mining performance.
People also ask:
Because it learns complex patterns automatically.
A model inspired by biological neurons that processes data through multiple layers.
CNNs.
RNNs, LSTMs, and Transformers.
Dimensionality reduction and anomaly detection.