Explore the History of cybersecurity from the first self-replicating Creeper program to Pakistan’s modern cybercrime laws under PECA 2016. Learn how digital defense evolved from simple code to a national priority.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Early History of Cybersecurity – Creeper and Reaper
- Key Terminology in Cybersecurity
- Information Security vs Cybersecurity
- Cybercrime and Its Motives
- Cybercrime Laws in Pakistan (PECA 2016)
- Conclusion – Lessons from the History of Cybersecurity
Introduction
The history of cybersecurity began long before most people even heard the word “internet.” When researchers linked computers through ARPANET in the 1970s, they also opened doors to the first digital threats. What started as harmless experimentation evolved into one of the most critical fields in modern technology protecting billions of connected devices and people worldwide.

The Early History of Cybersecurity – Creeper and Reaper
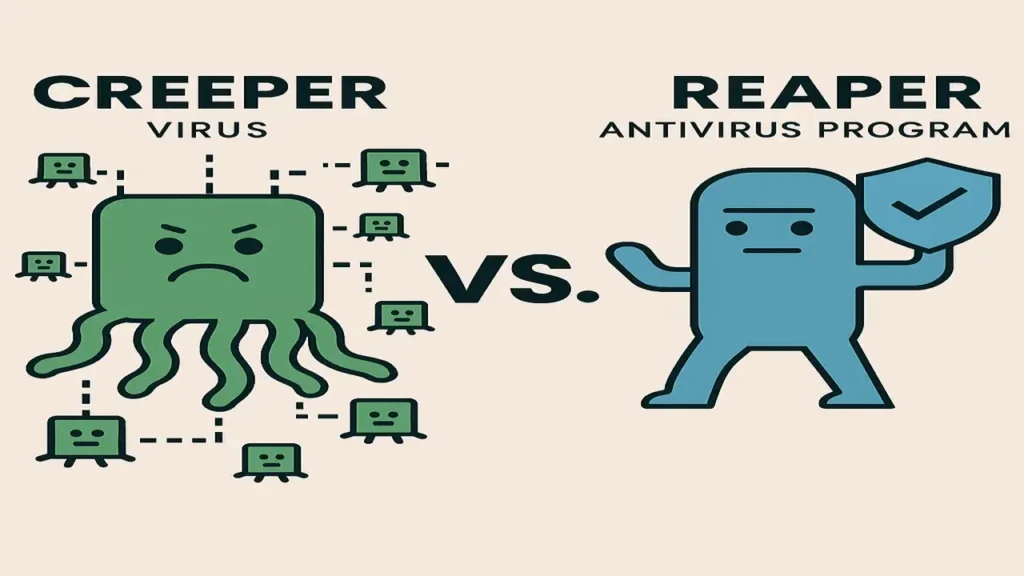
In the early 1970s, a program called Creeper became the world’s first self-replicating computer worm. It spread through ARPANET displaying the message, “I’m the Creeper, catch me if you can.”
To counter it, scientists created Reaper, the first antivirus program designed to track and delete Creeper.
This moment marked the birth of cyber defense, setting the stage for decades of innovation, attacks, and evolving protection strategies.
To understand the foundation of computing and cybersecurity, it’s also important to explore the Number System in Digital Logic Design
Key Terminology in Cybersecurity
To understand the history of cybersecurity, you must speak its language. Here are the most essential terms:
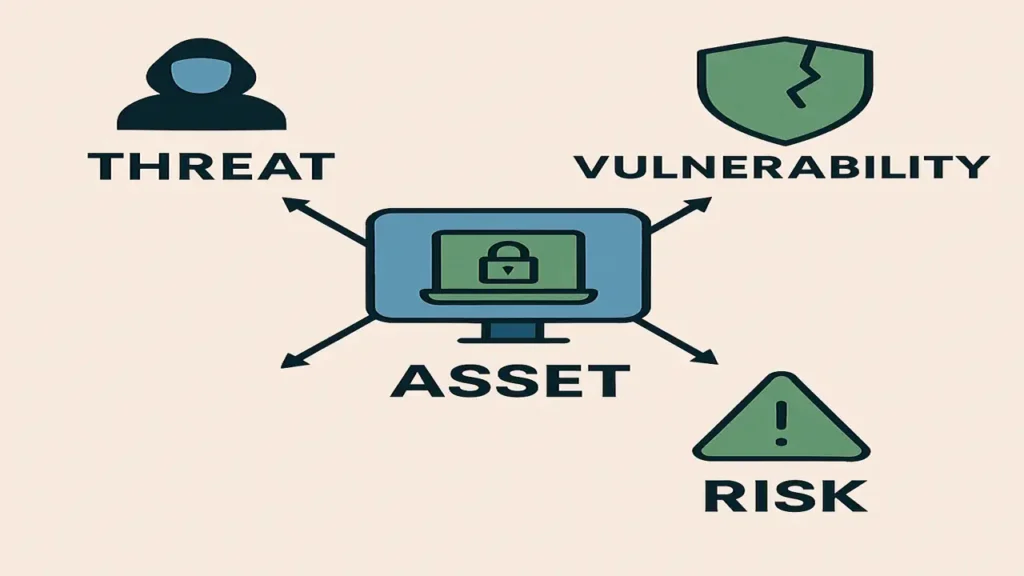
- Asset: Anything valuable that needs protection data, systems, or intellectual property.
- Vulnerability: A weakness in a system that could be exploited.
- Threat: A potential danger exploiting a weakness.
- Exploit: A technique used to trigger a vulnerability.
- Risk: The potential for loss or damage.
- Attack Vector: The route used by hackers to access systems.
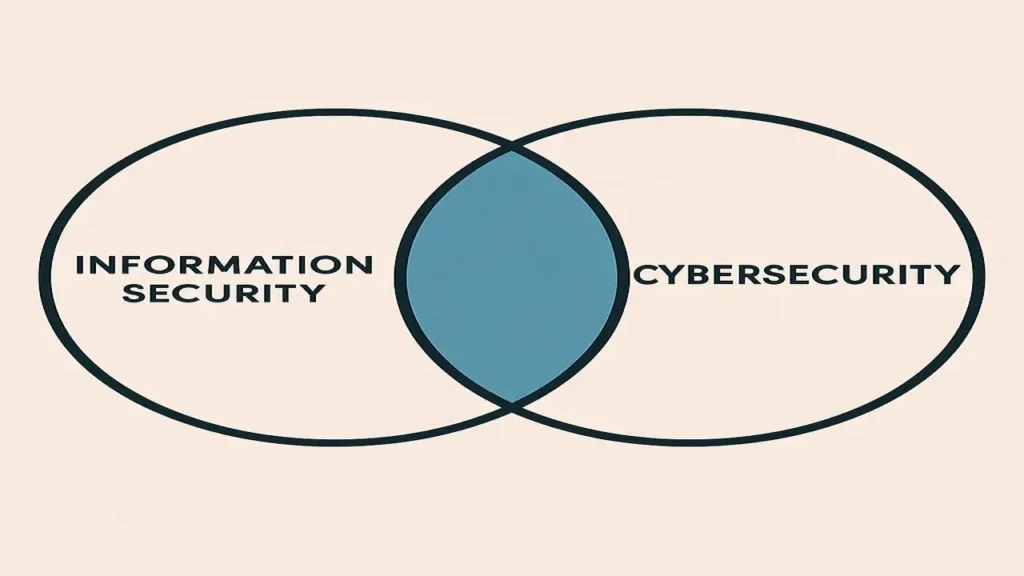
Information Security vs Cybersecurity
A common confusion in the history of cybersecurity is the difference between information security and cybersecurity.
- Information Security protects information in all forms digital, physical, or verbal.
- Cybersecurity focuses specifically on digital systems, data, and networks.
💡 In short: All cybersecurity is information security, but not all information security is cybersecurity.
Cybercrime and Its Motives
As the internet expanded, so did the number of people exploiting it. Understanding motives helps experts prevent attacks more effectively.
- Financial Gain: Ransomware, credit-card theft, and corporate espionage.
- Hacktivism: Promoting social or political causes.
- Espionage: State-sponsored data theft.
- Personal Reasons: Revenge, disruption, or notoriety.
Cybercriminals have grown from lone hackers to global networks a natural outcome of the evolving history of cybersecurity.

To strengthen the fundamentals of programming and AI, it’s essential to learn the Introduction to Data Structures
Cybercrime Laws in Pakistan (PECA 2016)
The history of cybersecurity in Pakistan changed forever with the Prevention of Electronic Crimes Act (PECA 2016). This law defines and punishes electronic crimes to protect citizens and organizations.
| Offense | Penalty |
|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Up to 3 years jail + ₨ 1 million fine |
| Unauthorized Copying or Data Transmission | Up to 6 months jail + ₨ 100 000 fine |
| Cyberstalking / Harassment | Up to 3 years jail + ₨ 1 million fine |
| Offences Against Dignity | Up to 3 years jail + ₨ 1 million fine |
| Cyber-Terrorism | Up to 14 years jail + ₨ 50 million fine |
| Malicious Code Distribution | Up to 2 years jail + ₨ 1 million fine |
The Federal Investigation Agency (FIA) is responsible for enforcing these laws.
📧 Contact: helpdesk.cyber@fia.gov.pk

Conclusion – Lessons from the History of Cybersecurity
From Creeper and Reaper to PECA 2016, the history of cybersecurity reflects how humanity learns, adapts, and strengthens with each threat. Every digital breakthrough brings new risks and with them, new solutions.
Defending our digital future requires awareness, education, and law enforcement working hand in hand. Cybersecurity is no longer optional; it’s a shared responsibility in today’s connected world.