Explore a detailed introduction to Artificial Intelligence, including its history, core components, intelligent agents, Machine Learning, and real-world applications.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries, redefining innovation, and reshaping the way humans interact with technology. From self-driving cars to intelligent chatbots, AI systems are becoming deeply embedded in modern society. This comprehensive article provides an in-depth introduction to Artificial Intelligence, its history, key components, working principles, and real-world applications.
If you are beginning your journey in AI, this guide will help you understand the foundational concepts and core components that define the field of Artificial Intelligence.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the branch of computer science that focuses on designing machines capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, perception, problem-solving, decision-making, and natural language understanding.
In simple terms, Artificial Intelligence enables machines to simulate human thinking and behavior. Unlike traditional computer programs that follow fixed instructions, AI systems can learn from data, adapt to new inputs, and improve their performance over time.
AI systems are designed to:
- Analyze large volumes of data
- Identify patterns and relationships
- Make intelligent decisions
- Adapt to changing environments
- Perform tasks autonomously
The History and Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
Understanding the history of Artificial Intelligence helps explain how the field evolved into today’s advanced AI systems.
Early Foundations of AI
The conceptual foundation of Artificial Intelligence began in the mid-20th century. In 1950, Alan Turing proposed the idea that machines could simulate human thinking. His famous Turing Test suggested that if a machine could imitate human responses convincingly, it could be considered intelligent.
In 1956, the Dartmouth Conference officially introduced the term “Artificial Intelligence,” marking the birth of AI as an academic discipline.
Symbolic AI and Expert Systems
During the 1960s and 1970s, AI research focused on symbolic reasoning and rule-based systems. Expert systems were developed to mimic decision-making abilities of human experts using logical rules.
Rise of Machine Learning
In the 1980s, the focus shifted toward Machine Learning, where systems learned patterns from data rather than relying solely on hardcoded rules.
Modern AI Era
The 21st century witnessed rapid advancements in:
- Deep Learning
- Neural Networks
- Natural Language Processing
- Computer Vision
- Autonomous Systems
Major milestones include:
- IBM’s Deep Blue defeating a chess champion
- Google’s AlphaGo beating a world Go champion
- The development of autonomous vehicles
- Breakthroughs in generative AI models
Artificial Intelligence continues to evolve rapidly, influencing nearly every industry.
Artificial Intelligence vs Traditional Programming
A key concept in understanding Artificial Intelligence is recognizing how it differs from traditional programming.
Traditional Programming
In traditional programming:
- Humans define explicit rules.
- The system follows step-by-step instructions.
- The output strictly depends on predefined logic.
- No learning occurs beyond programmed instructions.
Artificial Intelligence Systems
In Artificial Intelligence:
- Systems learn from data.
- Algorithms adapt and improve over time.
- Decision-making evolves with experience.
- AI can handle uncertainty and complex environments.
For example, in traditional programming, spam detection rules are manually written. In AI-based spam detection, the system learns patterns from thousands of emails and builds its own predictive model.
This learning capability is what makes Artificial Intelligence fundamentally different.
Key Components of Artificial Intelligence
To truly understand Artificial Intelligence, it is essential to understand its core components. These components form the foundation of AI systems.
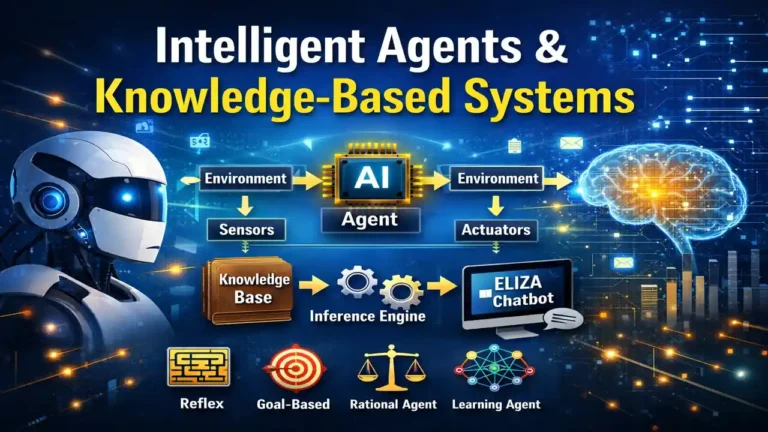
1. Intelligent Agents
An intelligent agent is an autonomous entity that:
- Perceives its environment
- Processes information
- Makes decisions
- Takes actions to achieve goals
An intelligent agent typically includes:
- Sensors (to gather input)
- Decision-making logic
- Actuators (to perform actions)
Examples of intelligent agents include:
- Self-driving cars
- Virtual assistants
- Robotic systems
- Game-playing AI
The concept of intelligent agents lies at the heart of Artificial Intelligence.
2. Machine Learning
Machine Learning is one of the most important components of Artificial Intelligence. It enables systems to learn from data without explicit programming.
Types of Machine Learning include:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Machine Learning allows AI systems to:
- Recognize patterns
- Predict outcomes
- Improve decision accuracy
- Adapt to new data
Most modern AI applications rely heavily on Machine Learning.
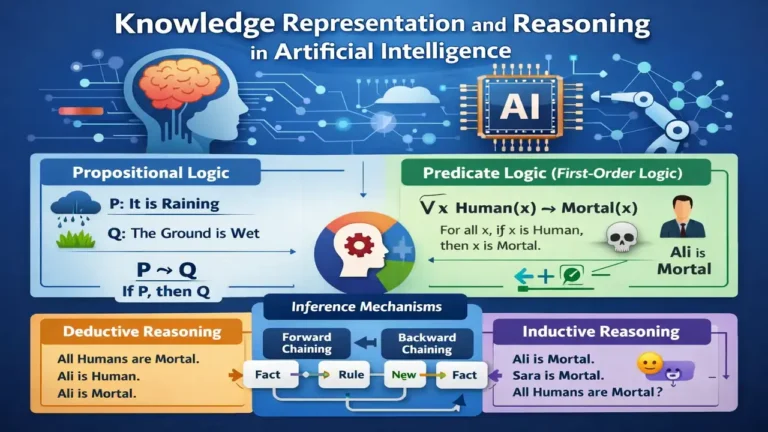
3. Knowledge Representation
Knowledge representation involves structuring and storing information in a way that enables reasoning.
AI systems use:
- Logical rules
- Knowledge bases
- Ontologies
- Semantic networks
Effective knowledge representation allows Artificial Intelligence systems to reason logically and solve problems efficiently.
4. Reasoning and Inference
Reasoning enables AI systems to draw conclusions from known facts.
Types of reasoning include:
- Deductive reasoning
- Inductive reasoning
- Probabilistic reasoning
Reasoning systems allow AI to simulate logical human thinking and support intelligent decision-making.
5. Search Algorithms
Many AI problems involve searching for the best possible solution within a large space.
Common search algorithms include:
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
- A* Search Algorithm
Search techniques are essential in:
- Game playing
- Pathfinding
- Planning systems
6. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Applications include:
- Chatbots
- Virtual assistants
- Machine translation
- Sentiment analysis
NLP bridges communication between humans and machines.
7. Computer Vision
Computer Vision allows Artificial Intelligence systems to interpret visual information.
Applications include:
- Facial recognition
- Medical image diagnosis
- Object detection
- Autonomous vehicle navigation
8. Robotics
Robotics integrates Artificial Intelligence with mechanical systems.
AI-driven robots can:
- Navigate environments
- Manipulate objects
- Perform industrial tasks
- Assist in surgery
Robotics represents the physical embodiment of AI.
Real-World Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence has applications across numerous industries.
Healthcare
- Disease detection
- Medical imaging analysis
- Robotic surgery
- Personalized treatment
Finance
- Fraud detection
- Risk assessment
- Algorithmic trading
Education
- Adaptive learning platforms
- Intelligent tutoring systems
- Automated grading
Transportation
- Self-driving vehicles
- Traffic management systems
- Route optimization
Business and Marketing
- Recommendation systems
- Customer behavior analysis
- Predictive analytics
AI continues to expand into new domains.
Benefits and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
- Increased efficiency
- Improved accuracy
- Automation of repetitive tasks
- Enhanced decision-making
- Continuous operation
Challenges of Artificial Intelligence
- Ethical concerns
- Data privacy risks
- Algorithmic bias
- High development cost
- Lack of transparency
Understanding both advantages and limitations is critical for responsible AI development.
Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence
As Artificial Intelligence grows more powerful, ethical considerations become increasingly important.
Key concerns include:
- Bias in AI systems
- Privacy violations
- Transparency and explainability
- Accountability in automated decisions
- Job displacement
Responsible AI development ensures fairness, safety, and societal benefit.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of Artificial Intelligence includes:
- Explainable AI systems
- Human-AI collaboration
- AI-driven medical breakthroughs
- Smart cities
- Sustainable AI technologies
- Advanced generative AI systems
Artificial Intelligence is expected to become even more integrated into daily life and global industries.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a rapidly evolving field that focuses on building intelligent systems capable of learning, reasoning, and acting autonomously. Understanding the key components of Artificial Intelligence such as intelligent agents, machine learning, knowledge representation, reasoning, search algorithms, NLP, computer vision, and robotics is essential for grasping the foundation of AI.
As AI continues to reshape industries and society, gaining a deep understanding of its principles and applications is more important than ever.
Artificial Intelligence is not just about machines it is about building intelligent systems that solve real-world problems and enhance human capabilities.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) – Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
1. Artificial Intelligence is primarily concerned with:
A) Building faster computers
B) Creating machines that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence
C) Designing hardware circuits
D) Developing computer games
Answer: B
2. The Turing Test was proposed by:
A) John McCarthy
B) Alan Turing
C) Marvin Minsky
D) Elon Musk
Answer: B
3. AI systems differ from traditional programs because AI systems:
A) Only use hardware
B) Follow fixed rules only
C) Can learn from data
D) Cannot process data
Answer: C
4. An intelligent agent primarily interacts with its:
A) Database
B) Environment
C) Compiler
D) Keyboard
Answer: B
5. Machine Learning is a subset of:
A) Networking
B) Artificial Intelligence
C) Operating Systems
D) Cybersecurity
Answer: B
6. Which of the following is an AI application?
A) Calculator
B) Chatbot
C) Notepad
D) Keyboard driver
Answer: B
7. Computer Vision enables machines to:
A) Hear sounds
B) Process text
C) Interpret images
D) Compile programs
Answer: C
8. The Dartmouth Conference (1956) is important because:
A) Internet was invented
B) AI term was introduced
C) First robot was built
D) First website launched
Answer: B
9. Natural Language Processing allows machines to:
A) Store memory
B) Understand human language
C) Design circuits
D) Run faster
Answer: B
10. Robotics integrates AI with:
A) Mathematics
B) Hardware systems
C) Databases
D) Software compilers
Answer: B
11. Which component allows AI systems to draw conclusions from known facts?
A) Networking
B) Reasoning
C) Storage
D) Debugging
Answer: B
12. In traditional programming, the output is determined by:
A) Data patterns
B) Machine learning
C) Predefined rules
D) Neural networks
Answer: C
13. An intelligent agent uses sensors to:
A) Store data
B) Perceive environment
C) Compile code
D) Install software
Answer: B
14. Which of the following is a search algorithm?
A) Sorting
B) BFS
C) Encryption
D) Compilation
Answer: B
15. Knowledge representation helps AI systems to:
A) Increase RAM
B) Reason logically
C) Improve graphics
D) Speed up internet
Answer: B
16. Which AI component is responsible for learning patterns from data?
A) Machine Learning
B) Robotics
C) Compiler
D) Firewall
Answer: A
17. Self-driving cars use AI mainly for:
A) Playing music
B) Environmental perception and decision-making
C) Typing documents
D) Printing reports
Answer: B
18. Which reasoning type derives specific conclusions from general rules?
A) Inductive
B) Deductive
C) Random
D) Predictive
Answer: B
19. NLP applications include:
A) Antivirus software
B) Image resizing
C) Chatbots
D) Hard disk formatting
Answer: C
20. AI systems improve performance through:
A) Manual programming only
B) Learning from data
C) Deleting files
D) Increasing hardware size
Answer: B
21. Which statement best describes Artificial Intelligence?
A) AI replaces all human jobs
B) AI simulates intelligent behavior in machines
C) AI only works with robots
D) AI is limited to games
Answer: B
22. The key difference between AI and traditional programming lies in:
A) Programming language
B) Learning capability
C) Hardware cost
D) Memory size
Answer: B
23. Which of the following is NOT a core component of AI?
A) Reasoning
B) Machine Learning
C) Knowledge Representation
D) Printer Drivers
Answer: D
24. An intelligent agent aims to:
A) Maximize goal achievement
B) Reduce electricity usage
C) Replace programmers
D) Install software
Answer: A
25. AI systems that interpret images rely mainly on:
A) NLP
B) Computer Vision
C) Firewall systems
D) Database indexing
Answer: B
26. Which of the following is an example of probabilistic reasoning?
A) 2 + 2 = 4
B) If A then B
C) Predicting rain based on probability
D) Compiling a program
Answer: C
27. The purpose of search algorithms in AI is to:
A) Delete files
B) Find optimal solutions
C) Compress images
D) Upgrade systems
Answer: B
28. Which AI application uses Natural Language Processing most directly?
A) Face recognition
B) Email spam filtering
C) Voice assistant
D) Hard disk scanning
Answer: C
29. Knowledge representation is important because it:
A) Increases hardware performance
B) Enables structured reasoning
C) Removes data
D) Improves internet speed
Answer: B
30. Which of the following best represents an intelligent agent system?
A) Calculator
B) Static webpage
C) Self-driving car
D) Text editor
Answer: C
SHORT QUESTIONS ANSWERS
1. Define Artificial Intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that focuses on developing machines capable of performing tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making.
AI systems analyze data, recognize patterns, and make intelligent decisions without being explicitly programmed for every situation.
Example: Self-driving cars and chatbots are applications of AI.
2. What is the Turing Test?
The Turing Test was proposed by Alan Turing in 1950 to evaluate a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to a human.
In this test, a human judge interacts with both a machine and a human through text. If the judge cannot reliably distinguish between them, the machine is considered intelligent.
The Turing Test measures a machine’s ability to imitate human responses.
3. Differentiate between Artificial Intelligence and Traditional Programming.
| Traditional Programming | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|
| Uses predefined rules | Learns from data |
| No adaptation | Improves over time |
| Deterministic output | Handles uncertainty |
| Human-written logic | Data-driven learning |
Traditional programming follows fixed instructions written by programmers. AI systems learn patterns from data and adapt their behavior based on experience.
Example: Manual spam filter vs AI-based spam detection.
4. What is an Intelligent Agent? Explain with example.
An Intelligent Agent is an autonomous system that perceives its environment through sensors and acts upon that environment through actuators to achieve specific goals.
It follows the cycle:
Perception → Decision → Action
Example: A self-driving car senses traffic using cameras, processes data, and controls steering and braking.
5. Explain Machine Learning.
Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence that enables systems to learn from data without explicit programming.
It allows machines to identify patterns, make predictions, and improve performance over time.
Types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Example: Email spam detection system.
6. What is Knowledge Representation?
Knowledge Representation is the method of structuring and storing information so that AI systems can reason and solve problems.
It uses:
- Logical rules
- Knowledge bases
- Ontologies
- Semantic networks
Effective knowledge representation enables intelligent decision-making.
7. Explain Deductive and Inductive Reasoning.
Deductive Reasoning:
Moves from general rule to specific conclusion.
Example:
All humans are mortal.
Ali is human.
Therefore, Ali is mortal.
Inductive Reasoning:
Moves from specific observations to general conclusion.
Example:
The sun has risen every day.
Therefore, the sun will rise tomorrow.
Deductive gives certain results; inductive gives probable results.
8. What are Search Algorithms in AI?
Search algorithms are techniques used in AI to find optimal solutions within a large problem space.
Common search algorithms include:
- Breadth First Search (BFS)
- Depth First Search (DFS)
- A* Algorithm
They are used in pathfinding, game playing, and planning systems.
9. Explain Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Applications include:
- Chatbots
- Voice assistants
- Machine translation
- Sentiment analysis
NLP bridges communication between humans and machines.
10. List four real-world applications of Artificial Intelligence.
- Self-driving vehicles
- Medical diagnosis systems
- Fraud detection in banking
- Recommendation systems (Netflix, Amazon)
AI is widely used in healthcare, finance, education, and transportation.
LONG QUESTIONS ANSWERS
1. Explain the Evolution of Artificial Intelligence.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. It has progressed from simple rule-based systems to advanced learning systems.
Early Foundations (1950s)
In 1950, Alan Turing introduced the concept of machine intelligence and proposed the Turing Test. In 1956, the Dartmouth Conference officially introduced the term “Artificial Intelligence.”
Symbolic AI Era (1960–1970)
AI research focused on rule-based systems and symbolic reasoning. Expert systems were developed to mimic human decision-making.
Rise of Machine Learning (1980s)
The focus shifted to systems that could learn from data rather than relying on hardcoded rules. Statistical models became popular.
Modern AI Era (21st Century)
Advancements include:
- Deep Learning
- Neural Networks
- Natural Language Processing
- Computer Vision
- Autonomous vehicles
- Generative AI
Major achievements include IBM Deep Blue and Google AlphaGo.
Conclusion
AI has evolved from rule-based logic systems to intelligent data-driven systems capable of solving complex real-world problems.
2. Explain the Key Components of Artificial Intelligence.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence consists of several components that enable machines to perform intelligent tasks.
1. Intelligent Agents
Autonomous systems that perceive and act to achieve goals.
2. Machine Learning
Allows systems to learn patterns from data.
3. Knowledge Representation
Structures information for logical reasoning.
4. Reasoning and Inference
Draws conclusions using logical methods.
5. Search Algorithms
Find optimal solutions in problem space (BFS, DFS, A*).
6. Natural Language Processing
Enables machines to understand human language.
7. Computer Vision
Interprets visual data such as images and videos.
8. Robotics
Integrates AI with physical machines.
Conclusion
These components collectively enable AI systems to learn, reason, and make intelligent decisions.
3. Differentiate Between AI and Traditional Programming. Why is AI More Powerful?
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence differs fundamentally from traditional programming in its approach to problem-solving.
Comparison
| Traditional Programming | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|
| Fixed rules | Learns from data |
| No adaptation | Self-improving |
| Deterministic | Handles uncertainty |
| Human-coded logic | Data-driven models |
Explanation
Traditional programs execute instructions exactly as written. AI systems learn patterns from data and adapt to new situations.
For example, in spam detection:
Traditional: Manually written rules.
AI: Learns from thousands of emails.
Why AI is More Powerful
- Handles complex environments
- Learns automatically
- Adapts to new data
- Works with uncertainty
Conclusion
AI is more powerful because it can learn, adapt, and improve, making it suitable for solving complex real-world problems.