Introduction to Problem Solving
Learn the basics of programming logic in this Introduction to Problem Solving guide. Explore algorithms, flowcharts, and real-life examples step-by-step.
What Is Problem Solving in Programming?
Problem solving in programming means finding a clear, logical path to reach a desired outcome before writing any code. It’s the process of understanding a problem, planning a solution, and testing it using algorithms or flowcharts.
Key Steps in Problem Solving:
- Identify the problem
- Analyze the problem
- Develop an algorithm
- (Optional) Use a flowchart
- Choose programming constructs
- Test with examples

→ Explore how modern hackers exploit system weaknesses and learn the defensive strategies every AI and CS student should understand The Powerful Anatomy of Cyber Threats & Attack Vectors (Part 1)
Step 1 – Identify and Analyze the Problem
The first step is understanding what needs to be solved.
Example:
“I need a program that calculates the average marks of 5 students.”
Break it down:
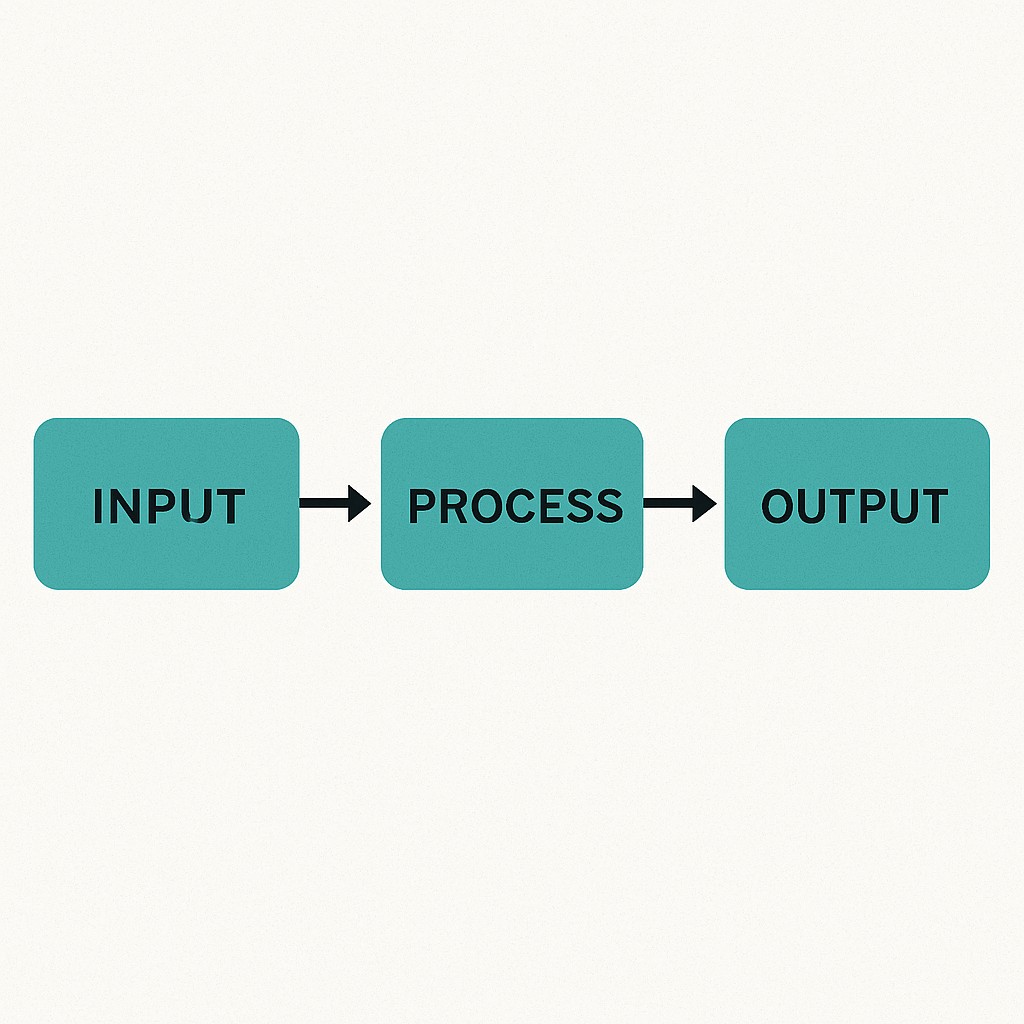
- Input: 5 marks
- Process: Add them and divide by 5
- Output: Average marks
This structure Input → Process → Output — is the core of all programs.
→ Discover how data structures form the building blocks of programming logic — the next step after mastering problem-solving fundamentals Introduction to Data Structures 2025
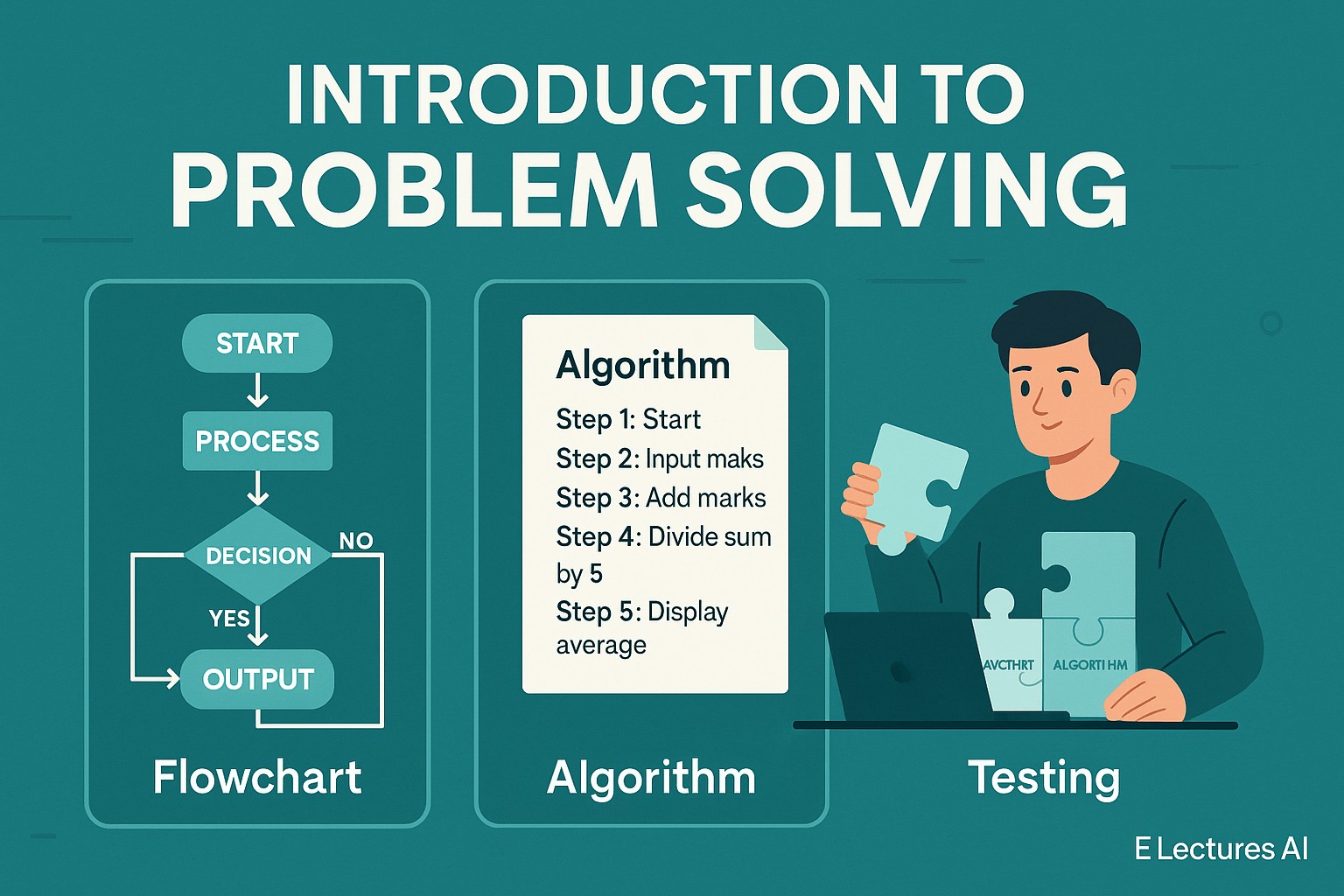
Step 2 – Develop an Algorithm
An algorithm is a step-by-step solution written in simple English (not code). It helps organize logic before programming.
Example Algorithm:
- Start
- Input 5 marks
- Add all marks
- Divide sum by 5
- Display average
- End
Why it Matters:
Algorithms save time, reduce errors, and improve clarity before you begin coding.

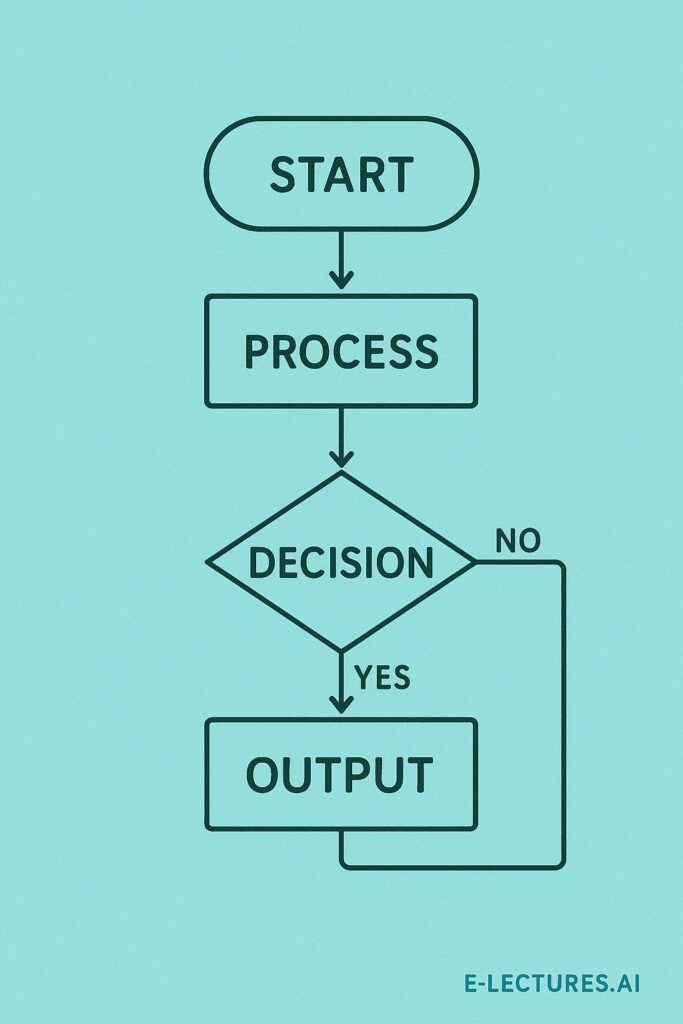
Step 3 – Use Flowcharts ( Optional )
A flowchart is a visual representation of your algorithm using shapes and arrows.
Common Flowchart Symbols:
| Shape | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Oval (Ellipse) | Start / End |
| Parallelogram | Input / Output |
| Rectangle | Process / Calculation |
| Diamond | Decision (Yes/No) |
Flowcharts make program logic easy to understand and debug.
→ Understand how logic gates and binary systems drive every computational process — the true foundation of artificial intelligence Digital Logic Design (DLD) – Foundation of Computing & AI
Step 4 – Choose Programming Constructs
After planning, decide how to implement your algorithm:
- Variables: Store data
- Conditions: Make decisions
- Loops: Repeat actions
- Functions: Organize tasks
This is where logic meets syntax in actual coding.
Step 5 – Test with Examples
Testing is the final phase. Try your algorithm with sample data to verify correctness.
Example:
If marks = 50, 60, 70, 80, 90
→ Sum = 350 → Average = 70

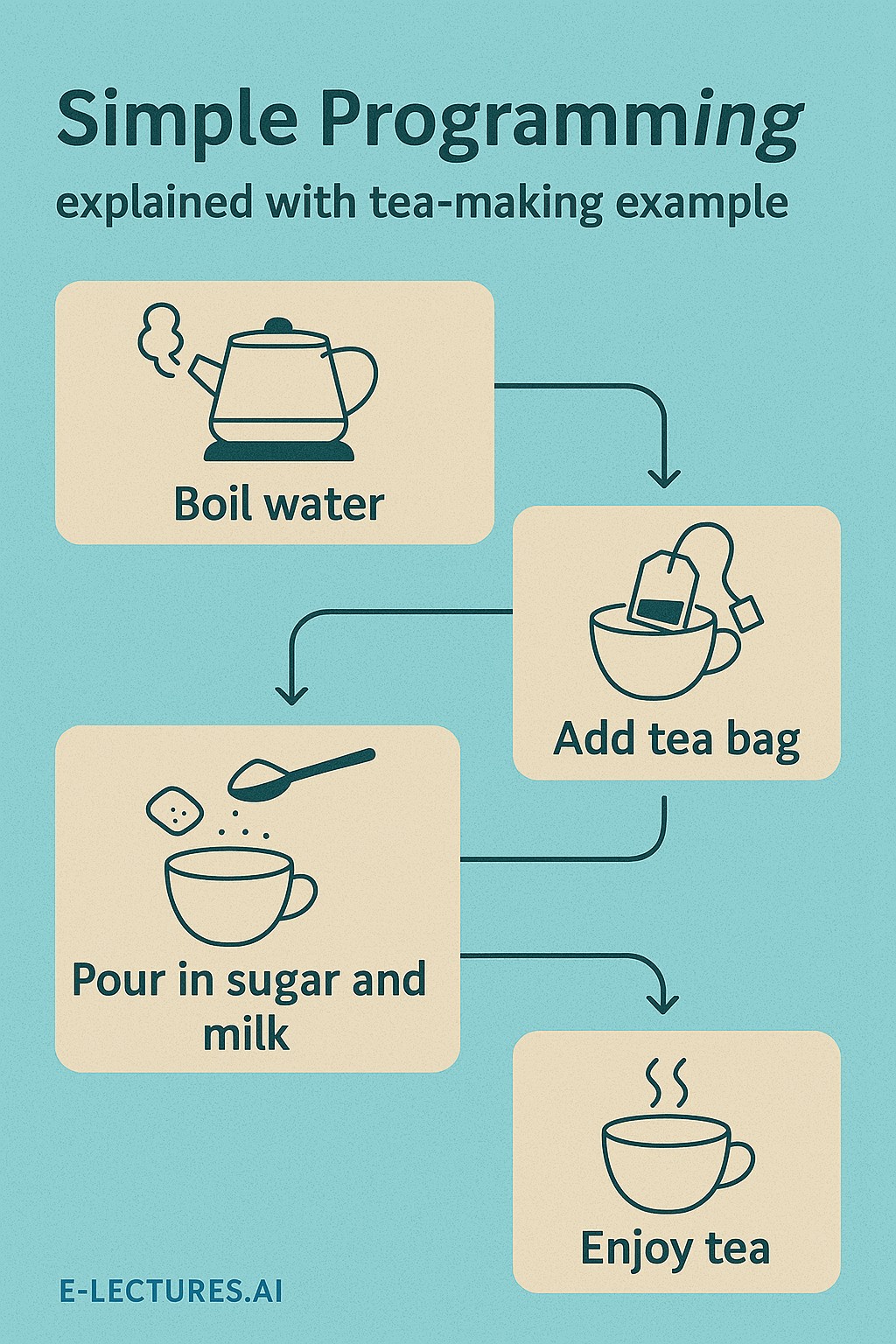
Real-Life Example – Making Tea
Programming logic exists everywhere — even in daily life!
Steps:
- Boil water
- Add tea leaves
- Add milk and sugar
- Stir well
- Serve tea
Input: Water, Milk, Sugar | Process: Boiling & Mixing | Output: Hot Tea
Why Problem Solving Matters
Programming is not about syntax — it’s about thinking logically and structuring solutions.
Benefits:
- Saves time and reduces errors
- Builds logical thinking
- Enhances creativity and precision
- Forms the foundation for coding and AI development

Summary
| Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Problem Solving | Planning the solution before coding |
| Algorithm | Step-by-step instructions |
| Flowchart | Visual logic representation |
| Testing | Ensuring accuracy and reliability |
In short:
“Good programmers don’t memorize syntax they master problem solving.”




Conditional Statements, Comments and Syntax in C++