Intelligent Requirements Engineering
Explore Intelligent Requirements Engineering Learn how AI and NLP automate requirement elicitation, ensure quality, and manage traceability in modern software engineering.
Automated Requirements Elicitation The Power of NLP
Traditional requirements elicitation often relies on manual interviews, workshops, or document analysis time-consuming processes prone to human bias and oversight.
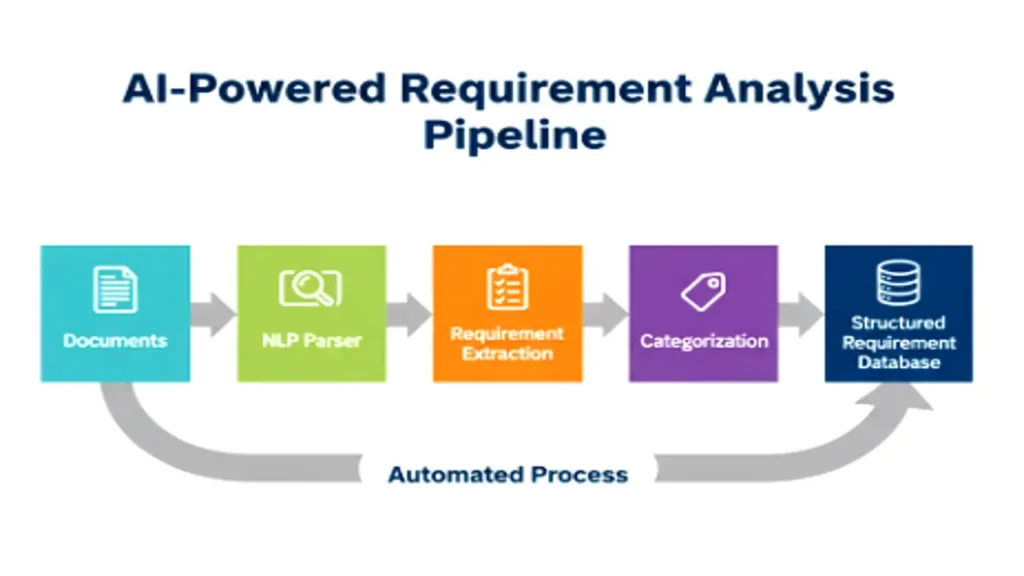
With NLP-based systems, engineers can automatically extract and categorize requirements from:
- Project specifications
- User stories
- Stakeholder emails and feedback
- Legacy documentation
How NLP Helps
- Entity and Intent Extraction: Identifies functional and non-functional requirements within text.
- Clustering and Topic Modeling: Groups similar requirements or detects missing ones.
- Semantic Search: Allows engineers to query documents in natural language.
Example: An NLP tool can scan a 200-page specification and extract sentences like “The system shall encrypt all user data” as security requirements, tagging them automatically for traceability.
Core AI/ML Concepts for Software Engineers
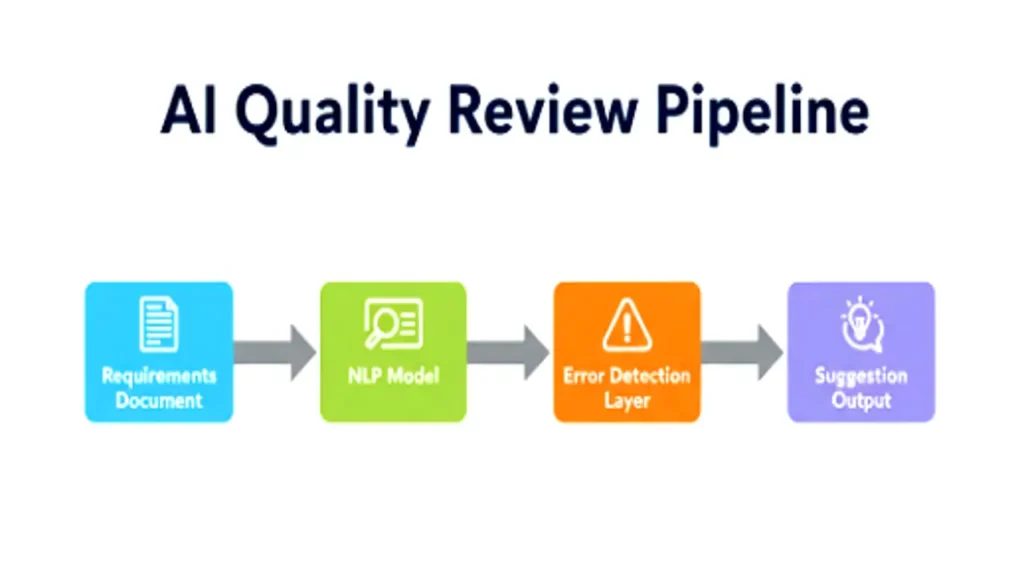
Requirements Quality Assurance with Machine Learning
Once requirements are gathered, ensuring clarity, consistency, and completeness is crucial.
ML models can now assess requirement quality by learning from thousands of labeled examples of well- and poorly-written requirements.
Common Quality Issues ML Can Detect
| Issue Type | Example | AI/ML Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Ambiguity | “System should be fast” | NLP models detect vague terms and suggest quantifiable metrics. |
| Inconsistency | One doc says “login required,” another says “guest access allowed.” | AI flags logical contradictions using semantic comparison. |
| Incomplete Requirement | Missing expected components like actor, action, or condition. | Grammar-aware ML models identify structural gaps. |
Real-World Use
- BERT-based classifiers evaluate requirement clarity.
- LLM-based checkers rewrite ambiguous requirements into precise forms.
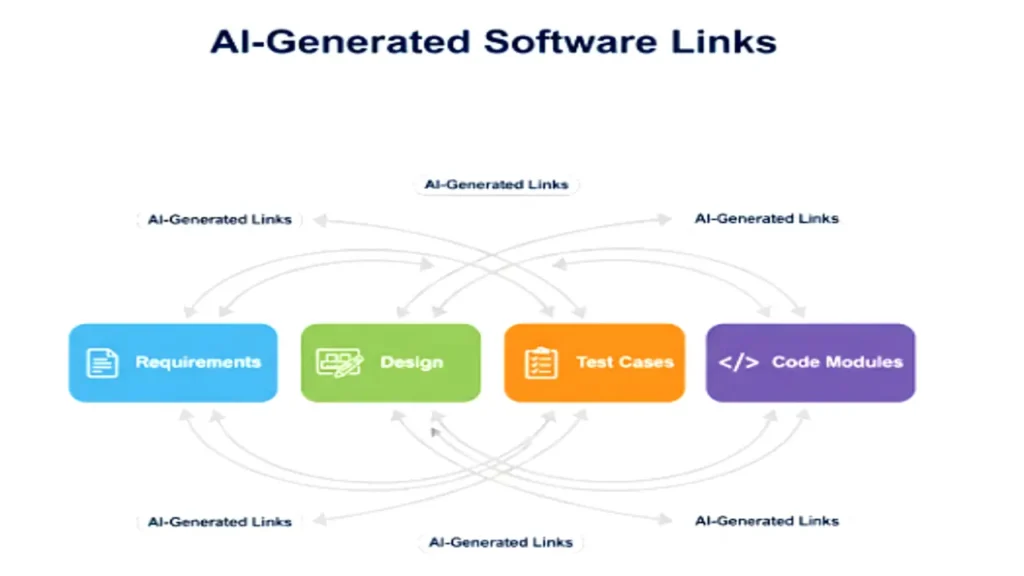
Intelligent Traceability Management
Traceability ensures every requirement is connected to design artifacts, test cases, and implementation modules. Traditionally maintained via spreadsheets or manual tagging, it’s often inconsistent and error-prone.
Intelligent Techniques for Traceability
- Semantic Similarity Matching: ML models link requirements to related design/test items using contextual embeddings (e.g., BERT, Sentence Transformers).
- Automated Impact Analysis: When one requirement changes, AI identifies affected code, documentation, or tests.
- Visual Trace Graphs: Interactive dashboards show relationships among artifacts dynamically.
Example: In a large-scale financial application, an AI traceability tool can automatically link the “Two-Factor Authentication” requirement to its corresponding API design, unit tests, and deployment policies.
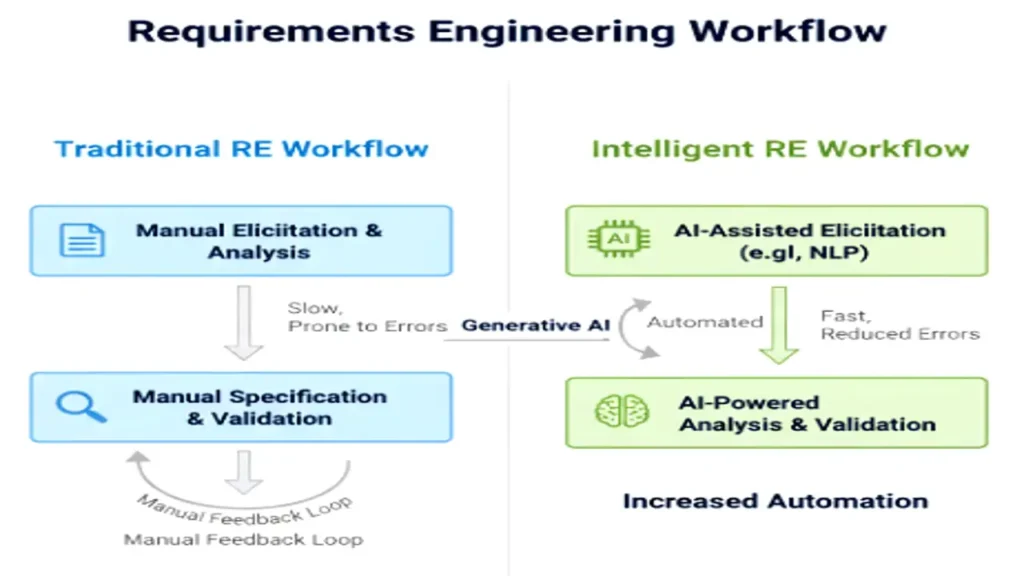
The Benefits of Intelligent RE
| Area | Traditional Approach | AI-Driven Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Elicitation | Manual, slow, text-heavy | NLP-based automated extraction |
| Validation | Peer reviews and meetings | ML-based ambiguity and conflict detection |
| Traceability | Manual mapping | Semantic and automated linkage |
| Change Management | Reactive updates | Predictive impact analysis |
AI transforms RE from a static documentation activity into a dynamic, learning system continuously improving as new data emerges.
Lecture Summary
- NLP automates requirement discovery from unstructured documents.
- ML models enhance clarity, detect inconsistencies, and flag missing requirements.
- Intelligent traceability tools maintain end-to-end visibility across the SDLC.
- The result: faster, smarter, and more adaptive software development lifecycles.
Core Insight: In Intelligent Software Engineering, AI doesn’t just understand code it understands intent.




