HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the foundation of every web page. It defines the structure and content of a website like the bones of a body.
In this lecture, you’ll learn:
- The basic structure of an HTML page
- How tags and attributes work
- The importance of semantic HTML
- How to create lists, tables, forms, and embed multimedia
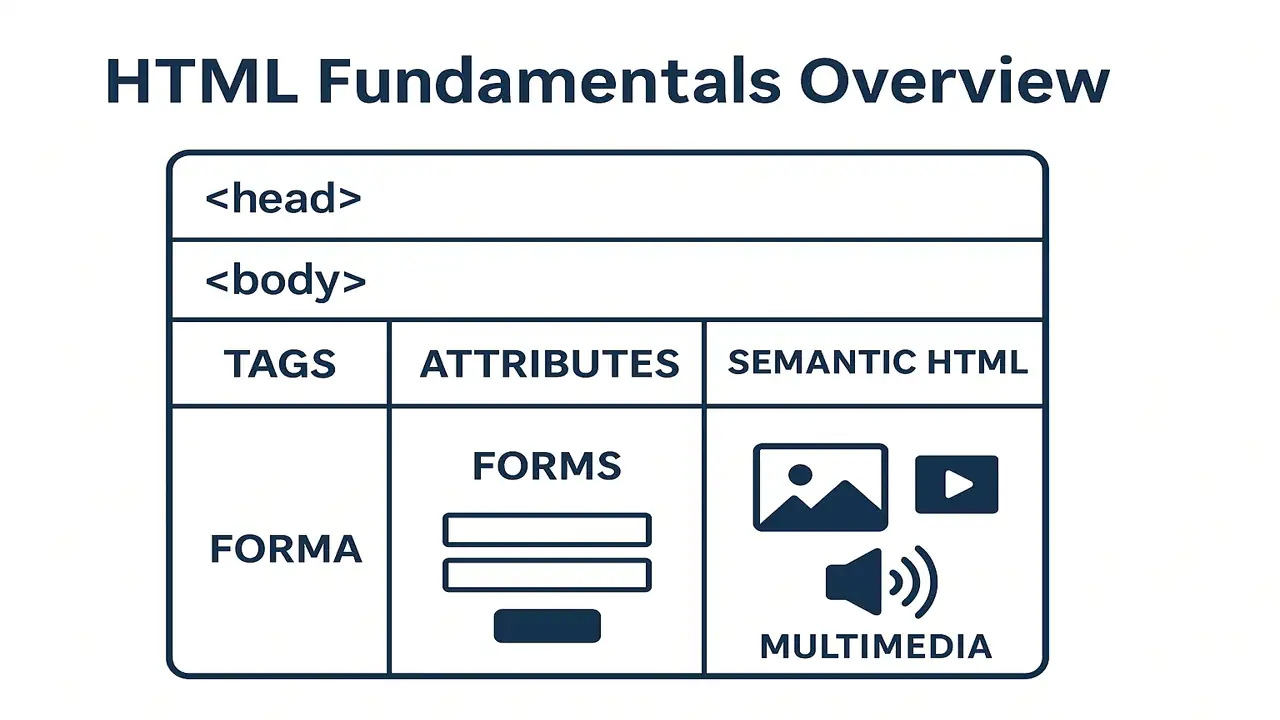
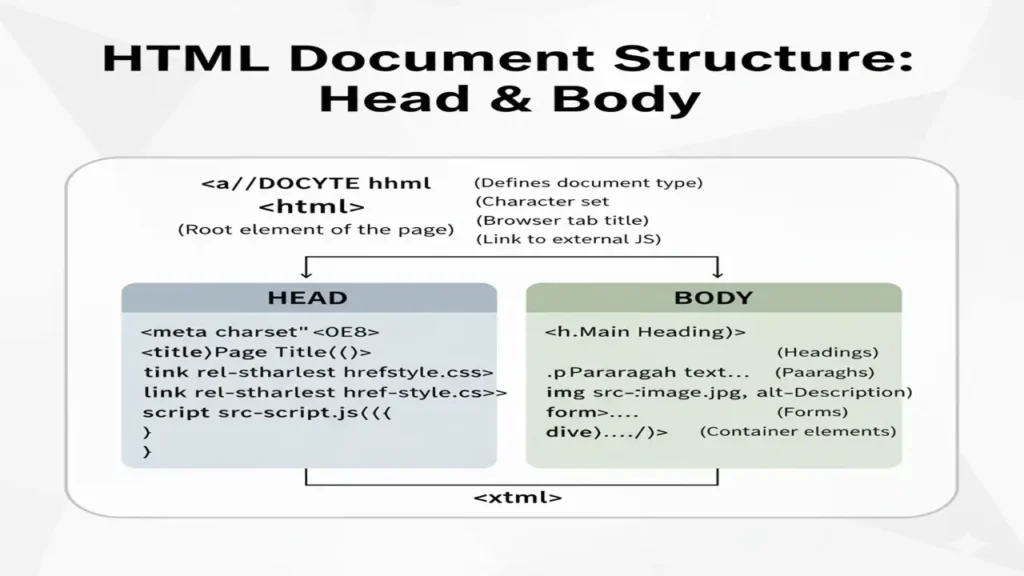
1. Basic Structure of an HTML Document
Every HTML page has a standard format that helps browsers understand what to display.
HTML Boilerplate Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First HTML Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
<p>This is my first web page.</p>
</body>
</html>As HTML plays a vital role in web designing, that is why html and web technology is deeply related so you need to know:
Introduction to Web Technologies
Explanation
<!DOCTYPE html>→ tells the browser it’s an HTML5 document.<html>→ root element of the page.<head>→ contains metadata (title, links, etc.).<body>→ displays the visible content.
2. Tags and Attributes
Tags
HTML elements are wrapped in tags that define their purpose.
Example:
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<h1>This is a heading.</h1>Attributes
Attributes give extra information to elements, written inside the opening tag.
Example:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Beautiful view">
<a href="https://electuresai.com">Visit ElecturesAI</a>src→ defines the image pathalt→ alternative text for accessibilityhref→ link destination

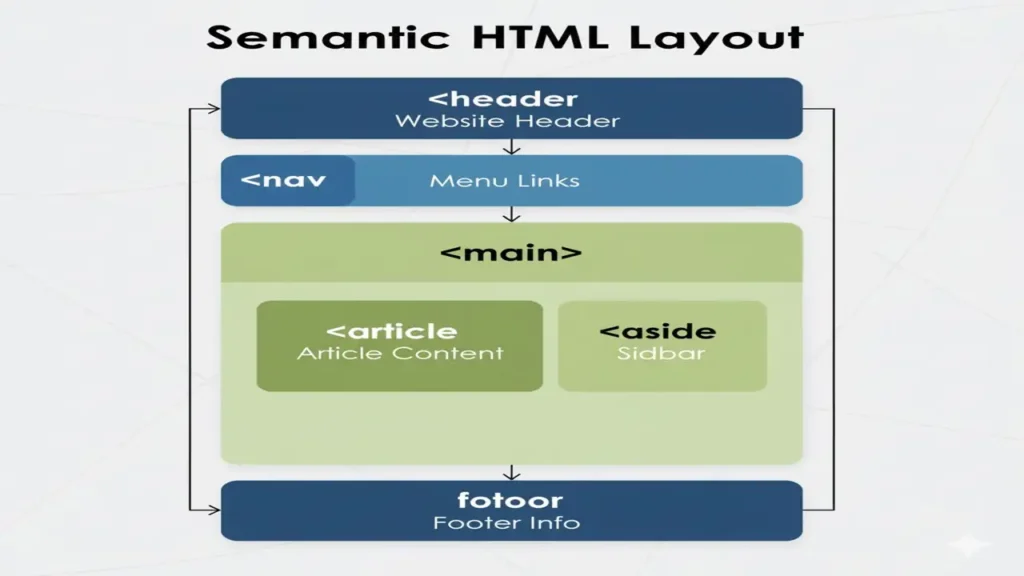
3. Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML adds meaning to your content, making it more readable for browsers and search engines.
Examples
<header>Site Header</header>
<nav>Navigation Links</nav>
<main>Main Content Area</main>
<article>Article Section</article>
<footer>Site Footer</footer>Why It’s Important
Improves accessibility
Boosts SEO ranking
Makes code more readable
When it comes to SEO and website’s ranking, you can see that how html help us to build user and Adsense friendly custom homepage click here to see html base homepage.
4. Lists in HTML
Lists organize content into structured points.
Types of Lists
- Ordered list (
<ol>) → numbered - Unordered list (
<ul>) → bullet points - Definition list (
<dl>) → term & definition
Example
<h3>Top 3 Web Technologies</h3>
<ol>
<li>HTML</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>JavaScript</li>
</ol>Output:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
5. Tables in HTML
Tables display data in rows and columns.
Example
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Language</th>
<th>Use</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>HTML</td>
<td>Structure</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>CSS</td>
<td>Design</td>
</tr>
</table>Output:
| Language | Use |
|---|---|
| HTML | Structure |
| CSS | Design |
6. Forms in HTML
Forms collect user input (e.g., login, registration).
Example
<form>
<label>Name:</label>
<input type="text" placeholder="Enter your name"><br>
<label>Email:</label>
<input type="email" placeholder="Enter your email"><br>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>Common Input Types
textemailpasswordradio/checkboxsubmit/button
7. Multimedia Elements
Multimedia makes web pages engaging using images, videos, and audio.
Examples
<img src="photo.jpg" alt="Nature Scene" width="400">
<video controls width="400">
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
</video>
<audio controls>
<source src="music.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
</audio>Conclusion
HTML is the foundation of every web page.
You’ve learned:
- The structure of an HTML document
- The use of tags and attributes
- The role of semantic HTML
- How to create lists, tables, forms, and multimedia
By mastering these, you can now build fully structured, content-rich web pages ready for styling and interactivity.
People also ask:
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It structures web pages by defining elements like headings, paragraphs, links, and images.
Tags define the structure of content, while attributes provide extra information about elements, such as src for images or href for links.
Block elements start on a new line and take full width, while inline elements stay within the same line without breaking the flow.