How pollution and waste management protect the environment. Learn air pollution sources, effects, and organic/inorganic pollutant control with Pakistan-specific examples.
Introduction to Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances or energy into the environment that causes adverse effects on living organisms and ecosystems.
It can be natural (volcanic ash, wildfires) or anthropogenic (industries, vehicles, agriculture).
Types:
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Soil pollution
- Noise and thermal pollution
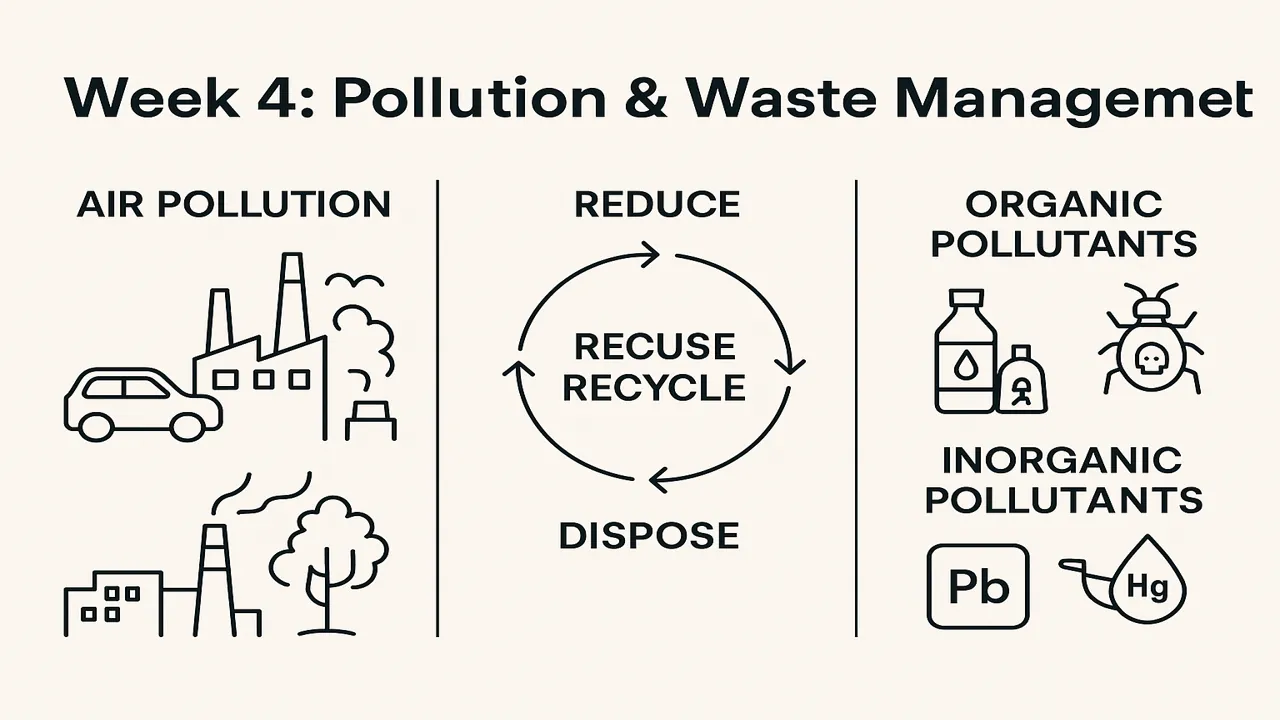
Air Pollution Sources and Effects
Primary pollutants: directly emitted (CO, SO₂, NOₓ, particulate matter, VOCs).
Secondary pollutants: form by reaction (ozone, photochemical smog).
Major sources in Pakistan:
- Transport: diesel and two-stroke engines (major smog cause in Punjab).
- Industry: brick kilns, cement factories, steel plants, power stations.
- Agriculture: burning of crop residues.
- Domestic: open waste burning, heating fuels (coal, wood).
Health & Environmental Effects:
- Respiratory diseases (asthma, bronchitis).
- Reduced visibility (smog).
- Acid rain damages crops and buildings.
- Global warming from CO₂ and CH₄ emissions.
Recent Event:
The 2023 Lahore Air Quality Index (AQI) exceeded 400 (“hazardous”), ranking among the world’s most polluted cities.
Waste Management
Definition: the collection, treatment, and disposal or recycling of waste materials.
Steps of Integrated Waste Management:
- Reduction: minimize at source.
- Reuse: extend product lifespan.
- Recycling: convert waste into usable material.
- Recovery: generate energy (biogas, compost).
- Disposal: safe landfill or incineration.
Pakistan Challenges:
- 30 million tons of solid waste annually, 60% from cities.
- Open dumping and burning common.
- Plastic bags banned but poorly enforced.
Solutions:
- Municipal waste segregation (organic vs inorganic).
- Composting of food waste.
- Circular economy: converting waste to raw material.
- Community awareness and 3R campaigns.
Week 3 – Environmental Threats, Global Climate Change, Pollution Dynamics, Pest and Pest Control
Organic and Inorganic Pollutants
| Type | Examples | Sources | Effects | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic | Pesticides, oil, plastics, detergents, sewage | Agriculture, households | Bioaccumulation, cancer, eutrophication | Biodegradation, phytoremediation |
| Inorganic | Heavy metals (Pb, Hg, Cd), acids, salts | Industry, mining, effluents | Toxic to fish, plants, humans | Chemical precipitation, ion exchange, neutralization |
Pollution Control Measures
- Technological: electrostatic precipitators, scrubbers, filters, catalytic converters.
- Administrative: emission standards, zoning, fines.
- Biological: green belts, afforestation, constructed wetlands.
- Personal: reduce, reuse, recycle, and avoid burning.
Pakistan Example:
The Pakistan Environmental Protection Act (PEPA) 1997 regulates emissions, while the Punjab Clean Air Plan 2023 targets brick kiln modernization and e-vehicle promotion.
Relationship Between Pollution and Waste
Poor waste handling creates secondary pollution:
- Burning waste → air pollution.
- Dumping waste → soil and water contamination.
- E-waste → toxic heavy metals.
Hence, integrated approaches link waste reduction with cleaner air and water.
Summary
Pollution and waste management are central to sustainable living. Air pollutants threaten health and climate; waste mismanagement worsens the crisis. A future-focused approach combines clean energy, strict laws, community behavior change, and circular economy models to achieve cleaner air, land, and water.
The approach followed at E Lectures reflects both academic depth and easy-to-understand explanations.
People also ask:
Unregulated transport emissions, industrial smoke, and crop residue burning are top causes.
By implementing 3Rs Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and supporting local composting initiatives.
Organic pollutants contain carbon compounds (biodegradable); inorganic are mineral-based (non-biodegradable).
Not entirely they cut tailpipe emissions but still need clean electricity sources.
Participate in clean-up drives, avoid single-use plastics, and spread awareness on recycling.