Learn conditional statements in Python with simple examples. This Lecture 4 guide explains if, elif, else, comparison operators, real-world use cases, MCQs, and practice questions for Data Science beginners.
What You Will Learn
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to:
- Understand why and where conditional statements are used
- Write if, elif, and else correctly
- Use comparison operators
- Apply logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
- Build real Data Science-style conditions
- Solve MCQs + practical exercises
1) What Are Conditional Statements?
A conditional statement allows Python to make a decision based on a condition.
Real-world examples:
- If rain starts → you open umbrella
- If battery < 15% → phone alerts
- If score ≥ 80 → Grade A
- If customer buys > 3 items → give discount
Python works exactly the same way.
2) IF Statement
Runs code only when condition is TRUE.
Example 1
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult")Example 2
marks = 95
if marks > 90:
print("Excellent!")3) IF–ELSE Statement
Used for two outcomes.
Example 1 – Pass / Fail
score = 40
if score >= 50:
print("Pass")
else:
print("Fail")Example 2 – Even / Odd
number = 11
if number % 2 == 0:
print("Even Number")
else:
print("Odd Number")4) IF–ELIF–ELSE Statement
Used when you have multiple conditions.
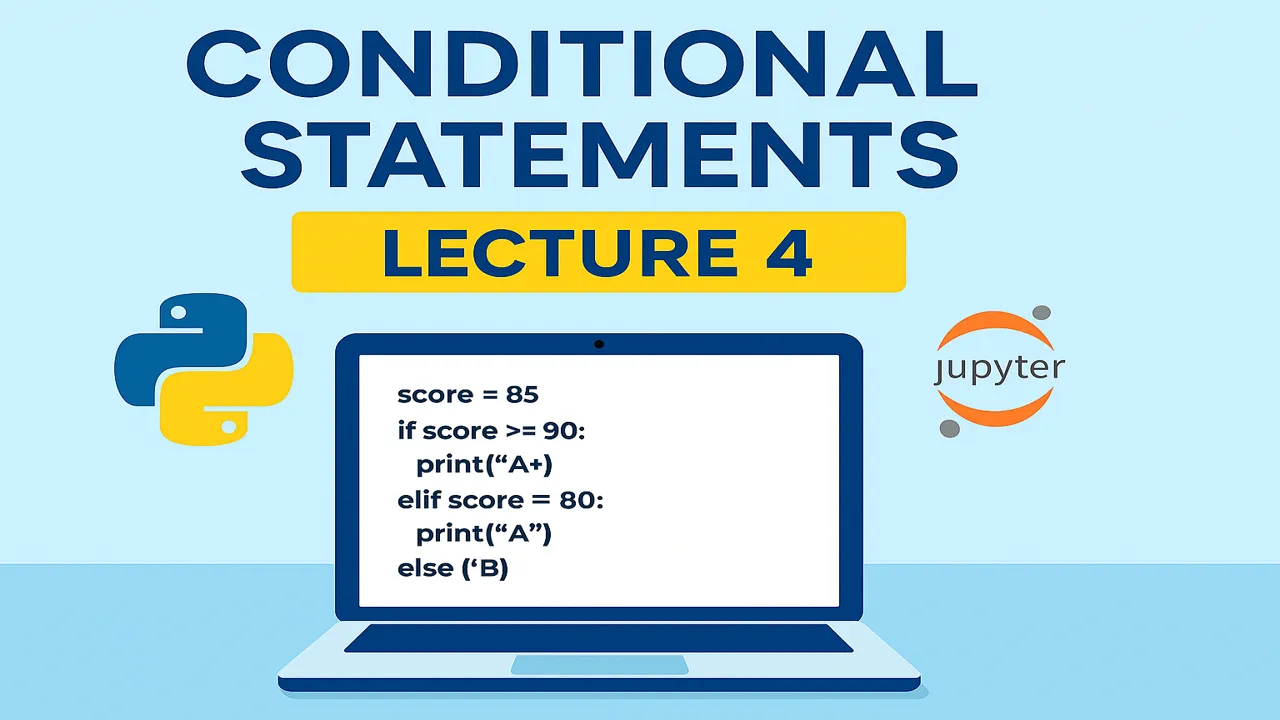
Example 1 – Grading
score = 85
if score >= 90:
print("A+")
elif score >= 80:
print("A")
elif score >= 70:
print("B")
else:
print("C")Example 2 – Temperature Classification
temp = 32
if temp > 40:
print("Very Hot")
elif temp > 30:
print("Warm")
elif temp > 20:
print("Normal")
else:
print("Cold")5) Comparison Operators
Used to compare values inside conditions.
| Operator | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
== | Equal | x == 10 |
!= | Not equal | x != 5 |
> | Greater than | x > 20 |
< | Less than | x < 15 |
>= | Greater or equal | x >= 18 |
<= | Less or equal | x <= 100 |
Lecture 3 – Python Data Structures (Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries)
6) Logical Operators (VERY IMPORTANT!)
Used when combining multiple conditions.
and → All conditions must be TRUE
or → At least one condition must be TRUE
not → Reverses the condition
Example – Admission Eligibility
marks = 85
age = 17
if marks >= 80 and age <= 18:
print("Eligible for admission")Example – Discount Eligibility
customer_type = "member"
amount = 5000
if customer_type == "member" or amount > 4000:
print("Discount applied!")Example – NOT
logged_in = False
if not logged_in:
print("Please log in first.")7) Real Data Science Examples
Example 1 – Categorizing BMI
bmi = 27
if bmi < 18.5:
print("Underweight")
elif bmi < 25:
print("Normal")
elif bmi < 30:
print("Overweight")
else:
print("Obese")Example 2 – Classifying Customer Spending
spent = 1200
if spent >= 2000:
print("Premium Customer")
elif spent >= 1000:
print("Regular Customer")
else:
print("Basic Customer")Example 3 – Weather Condition from Dataset
humidity = 82
if humidity > 90:
print("Rain Expected")
elif humidity > 70:
print("Humid")
else:
print("Normal Weather")Example 4 – Fraud Detection Logic
transaction_amount = 50000
location_changed = True
if transaction_amount > 30000 and location_changed:
print("High Risk Transaction")
else:
print("Normal Transaction")Quiz – Test Your Understanding
Instruction: First read the question and choose your answer. Then scroll down to see the correct answer
Which operator checks equality?
a) =
b) ==
c) !=
d) eq
Answer: b) ==
Which keyword is used for multiple conditions?
a) and
b) elif
c) else
d) check
Answer: b) elif
What will this print?
age = 16
if age >= 18:
print("Adult")
else:
print("Minor")a) Error
b) Adult
c) Minor
d) Nothing
Answer: c) Minor
What is the output?
x = 10
if x > 5 and x < 20:
print("Valid")
else:
print("Invalid")a) Valid
b) Invalid
c) Error
d) Both
Answer: a) Valid
Practice Questions
Instruction for students: Read the question, open your Jupyter Notebook, and try to solve it yourself. After that, come back and check the answer.
age = 17
if age >= 18:
print("Eligible")
else:
print("Not Eligible")units = 450
if units >= 500:
print("High Usage")
elif units >= 300:
print("Medium Usage")
else:
print("Low Usage")num = -4
if num > 0:
print("Positive")
elif num < 0:
print("Negative")
else:
print("Zero")marks = 92
attendance = 75
if marks >= 90 and attendance >= 80:
print("Top Student")
else:
print("Needs Improvement")



Very easy to learn. Thank you for sharing. Desperately waiting for next lecture