Environmental Biology topics remediation technologies, photochemical smog formation, and acid rain causes, effects, and solutions with Pakistan-specific examples.
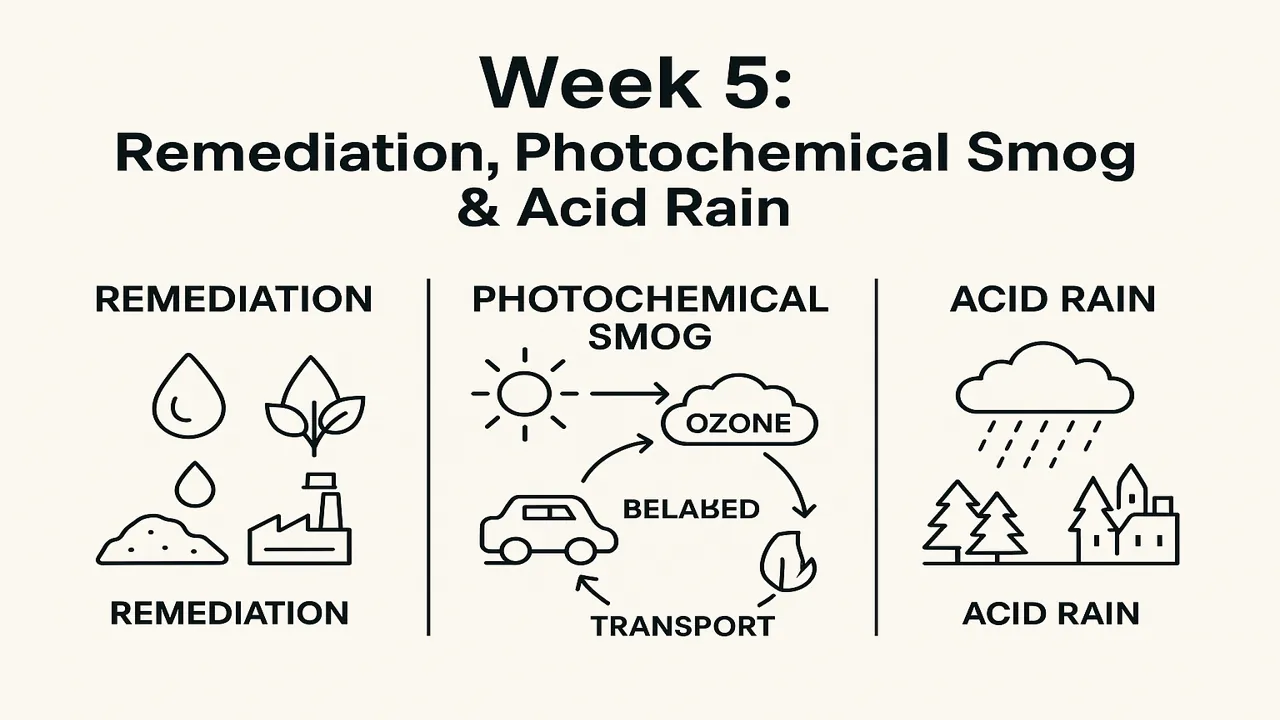
What Is Environmental Remediation?
Remediation means removing or neutralizing pollutants from soil, water, or air to restore environmental health.
Common Remediation Techniques:
| Type | Method | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Filtration, absorption, soil washing | Cleaning oil spills using absorbents |
| Chemical | Neutralization, oxidation-reduction | Adding lime to acidic soil |
| Biological | Bioremediation (microbes degrade pollutants) | Using bacteria to clean oil or pesticide residues |
| Phytoremediation | Plants absorb heavy metals | Sunflowers remove lead from soil |
Pakistan examples:
- Oil spill cleanup in Karachi coast (2018): microbial treatment used.
- Industrial soil treatment in Faisalabad: neutralization of textile effluent residues.
Photochemical Smog
Definition: A type of air pollution produced when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere to form ozone (O₃) and secondary pollutants.
Process (simplified):
- Emissions: vehicles, factories release NO₂ and hydrocarbons.
- Sunlight: UV radiation splits NO₂ → NO + O.
- Oxygen (O₂) reacts with O → O₃ (ozone).
- Ozone + hydrocarbons → peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) → eye irritation and plant damage.
Characteristics:
- Brownish haze seen in urban areas.
- Common in sunny, dry climates (e.g., Lahore smog season).
Health Impacts:
- Eye irritation, coughing, lung inflammation.
- Damages crops (especially wheat, spinach).
- Corrodes rubber and building materials.
Control Measures:
- Promote electric transport, CNG vehicles, public transit.
- Limit industrial emissions, enforce smog season bans.
- Tree plantation to absorb pollutants.
Acid Rain
Definition: Rainwater with pH < 5.6 due to the dissolution of acidic gases like SO₂ and NO₂ forming sulfuric (H₂SO₄) and nitric (HNO₃) acids.
Chemical Reactions:
SO₂ + O₂ → SO₃
SO₃ + H₂O → H₂SO₄
2NO₂ + H₂O → HNO₂ + HNO₃
Major Sources:
- Fossil fuel combustion (coal-based industries, vehicles).
- Smelting of ores.
- Thermal power plants.
Effects:
- Soil acidification: leaches essential nutrients.
- Aquatic life: fish kills due to pH drop.
- Infrastructure: corrodes marble and limestone monuments.
- Forests: weakens trees in hilly regions.
Example (Pakistan):
- Acidic rainfall episodes in Lahore and Faisalabad due to cross-border industrial emissions and urban vehicular smog.
Prevention:
- Use low-sulfur fuels.
- Install scrubbers and electrostatic precipitators.
- Shift to renewables.
- Cross-border cooperation (Pakistan-India Clean Air Dialogue).
Summary
Remediation restores the environment by removing pollutants. Photochemical smog and acid rain are two serious results of industrialization and fuel combustion, harming ecosystems, health, and materials. Sustainable technologies, emission reduction, and renewable energy are key to prevention.
The approach followed at E Lectures reflects both academic depth and easy-to-understand explanations.
People also ask:
Classical smog forms in humid, cool climates (London type), while photochemical smog occurs in sunny, dry areas (Los Angeles type).
Yes, it increases metal solubility (lead, copper), making water unsafe.
Chemical neutralization and bioremediation using bacteria and plants.
Smog includes chemical pollutants; haze is primarily fine dust particles.
By conducting awareness drives, planting trees, and promoting carpooling or cycling.